Ortelius Blog
Topics include Supply Chain Security, Microservice Management, Neat Tricks, and Contributor insights.
How to Bake an Ortelius Pi Part 5 | Ortelius Marries Jenkins
- Introduction
- Jenkins
- Gimlet GitOps Infrastructure
- Deploy Jenkins
- Plugins
- Helm-Repository | Jenkins
- Helm-Release | Jenkins
- Helm Chart Configuration Highlights
- Fluxcd is doing the following under the hood | Jenkins
- Kubernetes check | Jenkins
- How do we login?
- Jenkins admin password change
- Jenkins GitHub Setup
- Jenkins Agent Setup
- Jenkins Backup Setup
- Jenkins Restore
- Creating a Multibranch Pipeline
- Jenkins meets Ortelius
- Conclusion
- Next Steps
Introduction
In part 4 we configured a certificate for our domain using Cloudflare, LetsEncrypt and Traefik.
In part 5 we will deploy Jenkins on our Kubernetes cluster and configure integration with Ortelius and GitHub. We will then build a demo application and have Ortelius record it.
Jenkins
Jenkins is an open-source automation server that helps developers build, test, and deploy their software reliably and efficiently. It’s widely known for its role in continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD), allowing teams to automate tasks, improve workflows, and streamline software development pipelines.
Below we can see a typical architecture that you might find in the wild.
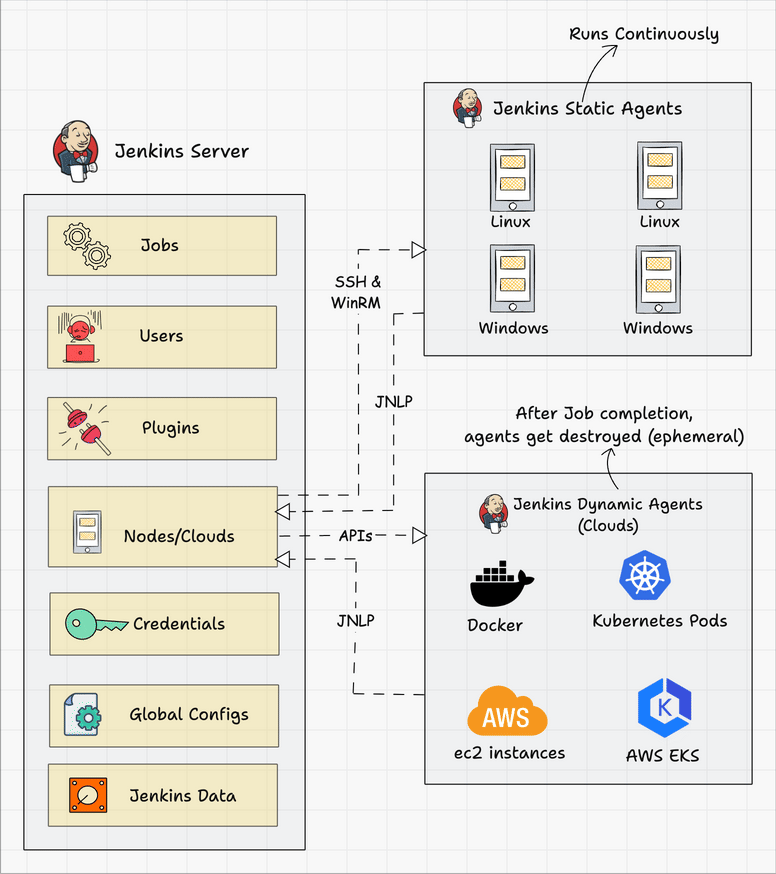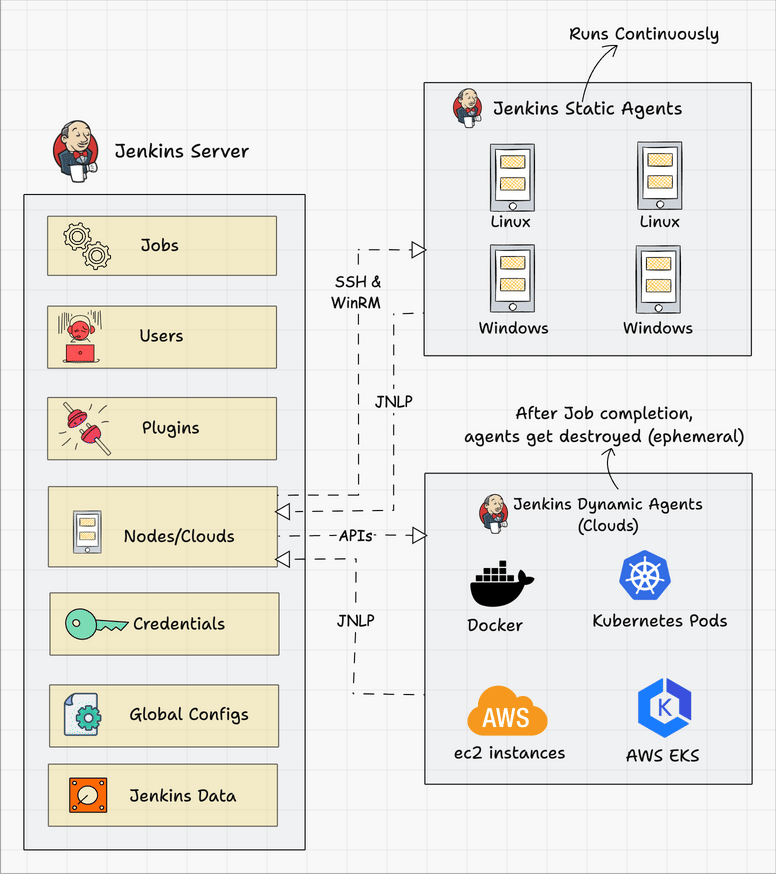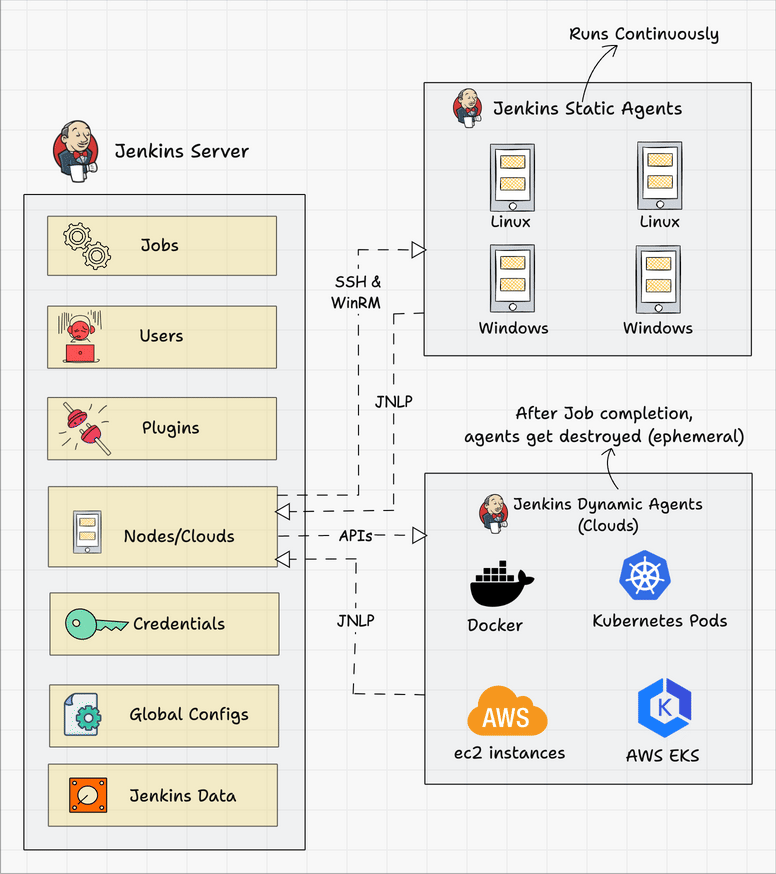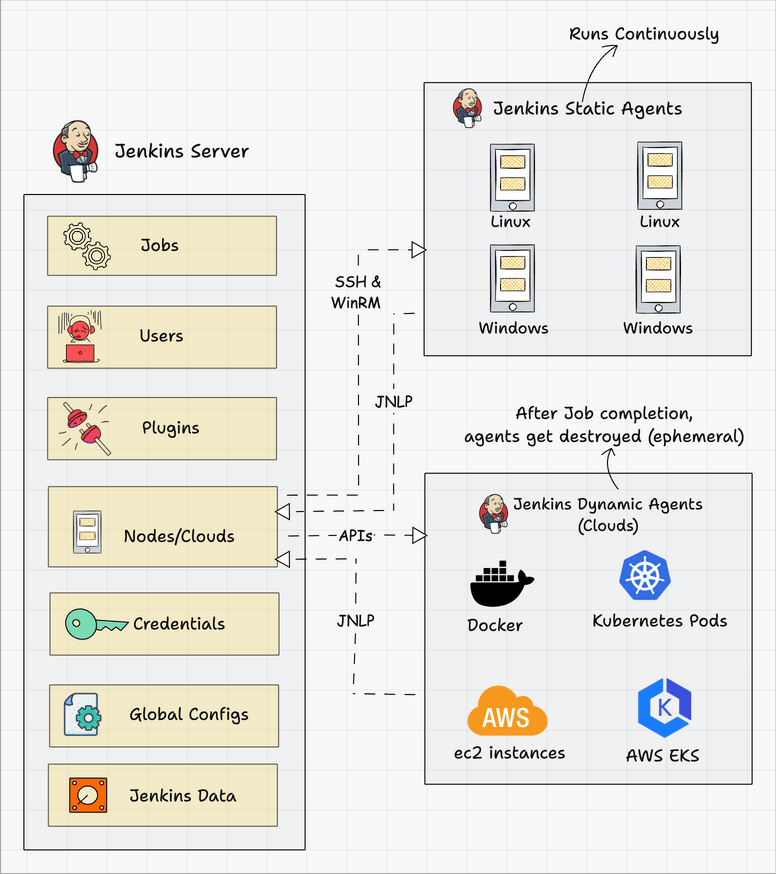
Connecting a Jenkins master and agent involves setting up the Jenkins master server to distribute tasks to agents for execution. Jenkins agents help offload work from the master, allowing for parallel execution of jobs, and can be set up to handle specific tasks such as building on different platforms or environments. You can either use SSH, Java Web Start (JNLP), or a custom agent setup for communication.
Gimlet GitOps Infrastructure
Deploy Jenkins
Right lets get stuck in and deploy Jenkins using Gimlet, Fluxcd, Helm and a sprig of GitOps. Just before we start I can thoroughly recommend this course to start your journey with becoming Jenkins savvy Jenkins Course (Zero To Production Ready)
- Kubectl quick reference guide here
- Helm cheat sheet here
- Jenkins on GitHub here
- Jenkins docs here
- Jenkins Helm Chart on ArtifactHub here
- Jenkins Plugins here
Plugins
Jenkins plugins are add-ons that extend the core functionality of Jenkins. Plugins allow Jenkins to integrate with various tools, languages, and services that you may use in your development pipeline. Plugins can be added through the GUI without being affected by Fluxcd’s drift detection.
Helm-Repository | Jenkins
- Lets add the Jenkins Helm repository
- A Helm repository is a collection of Helm charts that are made available for download and installation
- Helm repositories serve as centralised locations where Helm charts can be stored, shared, and managed
- Create a file called
jenkins.yamlin the helm-repositories directory and paste the following YAML
---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta1
kind: HelmRepository
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: infrastructure
spec:
interval: 60m
url: https://charts.jenkins.io
Helm-Release | Jenkins
- Lets create a Helm release for Jenkins
- A Helm release is an instance of a Helm chart running in a Kubernetes cluster
- Each release is a deployment of a particular version of a chart with a specific configuration
- Create a file called
jenkins.yamlin the helm-releases directory and paste the following YAML
Helm Chart Configuration Highlights
# -- Ingress annotations
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: traefik # Only change this if you are not using Traefik
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
# For Kubernetes >= 1.18 you should specify the ingress-controller via the field ingressClassName
# See https://kubernetes.io/blog/2020/04/02/improvements-to-the-ingress-api-in-kubernetes-1.18/#specifying-the-class-of-an-ingress
# ingressClassName: nginx
# Set this path to jenkinsUriPrefix above or use annotations to rewrite path
# -- Ingress path
path:
# configures the hostname e.g. jenkins.example.com
# -- Ingress hostname
hostName: jenkins.pangarabbit.com # Update this to your domain name
##RECOMMENDED##
##########################################################################################################################
# If your CSI NFS Kubernetes driver is setup correctly and you enabled persistence in the Helm Chart your Jenkins server #
# configuration files will be stored on your NFS server thus preserving your Jenkins configuration #
##########################################################################################################################
persistence:
# -- Enable the use of a Jenkins PVC
enabled: true
# A manually managed Persistent Volume and Claim
# Requires persistence.enabled: true
# If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
# -- Provide the name of a PVC
existingClaim:
# jenkins data Persistent Volume Storage Class
# If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
# If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
# If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
# set, choosing the default provisioner (gp2 on AWS, standard on GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
# -- Storage class for the PVC
storageClass: nfs-csi-jenkins # Replace with your storage class
# -- Annotations for the PVC
---
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta2
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: infrastructure
spec:
interval: 60m
releaseName: jenkins
chart:
spec:
chart: jenkins
version: v5.5.14 # Simply change the version to upgrade
sourceRef:
kind: HelmRepository
name: jenkins
interval: 10m
values:
# Default values for jenkins.
# This is a YAML-formatted file.
# Declare name/value pairs to be passed into your templates.
# name: value
## Overrides for generated resource names
# See templates/_helpers.tpl
# -- Override the resource name prefix
# @default -- `Chart.Name`
nameOverride:
# -- Override the full resource names
# @default -- `jenkins-(release-name)` or `jenkins` if the release-name is `jenkins`
fullnameOverride:
# -- Override the deployment namespace
# @default -- `Release.Namespace`
namespaceOverride:
# For FQDN resolving of the controller service. Change this value to match your existing configuration.
# ref: https://github.com/kubernetes/dns/blob/master/docs/specification.md
# -- Override the cluster name for FQDN resolving
clusterZone: "cluster.local"
# -- The URL of the Kubernetes API server
kubernetesURL: "https://kubernetes.default"
# -- The Jenkins credentials to access the Kubernetes API server. For the default cluster it is not needed.
credentialsId:
# -- Enables rendering of the helm.sh/chart label to the annotations
renderHelmLabels: true
controller:
# -- Used for label app.kubernetes.io/component
componentName: "jenkins-controller"
image:
# -- Controller image registry
registry: "docker.io"
# -- Controller image repository
repository: "jenkins/jenkins"
# -- Controller image tag override; i.e., tag: "2.440.1-jdk17"
tag:
# -- Controller image tag label
tagLabel: jdk17
# -- Controller image pull policy
pullPolicy: "Always"
# -- Controller image pull secret
imagePullSecretName:
# -- Lifecycle specification for controller-container
lifecycle: {}
# postStart:
# exec:
# command:
# - "uname"
# - "-a"
# -- Disable use of remember me
disableRememberMe: false
# -- Set Number of executors
numExecutors: 0
# -- Sets the executor mode of the Jenkins node. Possible values are "NORMAL" or "EXCLUSIVE"
executorMode: "NORMAL"
# -- Append Jenkins labels to the controller
customJenkinsLabels: []
hostNetworking: false
# When enabling LDAP or another non-Jenkins identity source, the built-in admin account will no longer exist.
# If you disable the non-Jenkins identity store and instead use the Jenkins internal one,
# you should revert controller.admin.username to your preferred admin user:
admin:
# -- Admin username created as a secret if `controller.admin.createSecret` is true
username: "admin"
# -- Admin password created as a secret if `controller.admin.createSecret` is true
# @default -- <random password>
password:
# -- The key in the existing admin secret containing the username
userKey: jenkins-admin-user
# -- The key in the existing admin secret containing the password
passwordKey: jenkins-admin-password
# The default configuration uses this secret to configure an admin user
# If you don't need that user or use a different security realm, then you can disable it
# -- Create secret for admin user
createSecret: true
# -- The name of an existing secret containing the admin credentials
existingSecret: ""
# -- Email address for the administrator of the Jenkins instance
jenkinsAdminEmail:
# This value should not be changed unless you use your custom image of jenkins or any derived from.
# If you want to use Cloudbees Jenkins Distribution docker, you should set jenkinsHome: "/var/cloudbees-jenkins-distribution"
# -- Custom Jenkins home path
jenkinsHome: "/var/jenkins_home"
# This value should not be changed unless you use your custom image of jenkins or any derived from.
# If you want to use Cloudbees Jenkins Distribution docker, you should set jenkinsRef: "/usr/share/cloudbees-jenkins-distribution/ref"
# -- Custom Jenkins reference path
jenkinsRef: "/usr/share/jenkins/ref"
# Path to the jenkins war file which is used by jenkins-plugin-cli.
jenkinsWar: "/usr/share/jenkins/jenkins.war"
# Override the default arguments passed to the war
# overrideArgs:
# - --httpPort=8080
# -- Resource allocation (Requests and Limits)
resources:
requests:
cpu: "50m"
memory: "256Mi"
limits:
cpu: "2000m"
memory: "4096Mi"
# Share process namespace to allow sidecar containers to interact with processes in other containers in the same pod
shareProcessNamespace: true
# Overrides the init container default values
# -- Resources allocation (Requests and Limits) for Init Container
initContainerResources: {}
# initContainerResources:
# requests:
# cpu: "50m"
# memory: "256Mi"
# limits:
# cpu: "2000m"
# memory: "4096Mi"
# -- Environment variable sources for Init Container
initContainerEnvFrom: []
# useful for i.e., http_proxy
# -- Environment variables for Init Container
initContainerEnv: []
# initContainerEnv:
# - name: http_proxy
# value: "http://192.168.64.1:3128"
# -- Environment variable sources for Jenkins Container
containerEnvFrom: []
# -- Environment variables for Jenkins Container
containerEnv: []
# - name: http_proxy
# value: "http://192.168.64.1:3128"
# Set min/max heap here if needed with "-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
# -- Append to `JAVA_OPTS` env var
javaOpts:
# -- Append to `JENKINS_OPTS` env var
jenkinsOpts:
# If you are using the ingress definitions provided by this chart via the `controller.ingress` block,
# the configured hostname will be the ingress hostname starting with `https://`
# or `http://` depending on the `tls` configuration.
# The Protocol can be overwritten by specifying `controller.jenkinsUrlProtocol`.
# -- Set protocol for Jenkins URL; `https` if `controller.ingress.tls`, `http` otherwise
jenkinsUrlProtocol:
# -- Set Jenkins URL if you are not using the ingress definitions provided by the chart
jenkinsUrl:
# If you set this prefix and use ingress controller, then you might want to set the ingress path below
# I.e., "/jenkins"
# -- Root URI Jenkins will be served on
jenkinsUriPrefix:
# -- Enable pod security context (must be `true` if podSecurityContextOverride, runAsUser or fsGroup are set)
usePodSecurityContext: true
# Note that `runAsUser`, `fsGroup`, and `securityContextCapabilities` are
# being deprecated and replaced by `podSecurityContextOverride`.
# Set runAsUser to 1000 to let Jenkins run as non-root user 'jenkins', which exists in 'jenkins/jenkins' docker image.
# When configuring runAsUser to a different value than 0 also set fsGroup to the same value:
# -- Deprecated in favor of `controller.podSecurityContextOverride`. uid that jenkins runs with.
runAsUser: 1000
# -- Deprecated in favor of `controller.podSecurityContextOverride`. uid that will be used for persistent volume.
fsGroup: 1000
# If you have PodSecurityPolicies that require dropping of capabilities as suggested by CIS K8s benchmark, put them here
# securityContextCapabilities:
# drop:
# - NET_RAW
securityContextCapabilities: {}
# In the case of mounting an ext4 filesystem, it might be desirable to use `supplementalGroups` instead of `fsGroup` in
# the `securityContext` block: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/67014#issuecomment-589915496
# podSecurityContextOverride:
# runAsUser: 1000
# runAsNonRoot: true
# supplementalGroups: [1000]
# capabilities: {}
# -- Completely overwrites the contents of the pod security context, ignoring the values provided for `runAsUser`, `fsGroup`, and `securityContextCapabilities`
podSecurityContextOverride: ~
# -- Allow controlling the securityContext for the jenkins container
containerSecurityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
runAsGroup: 1000
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
# For minikube, set this to NodePort, elsewhere uses LoadBalancer
# Use ClusterIP if your setup includes ingress controller
# -- k8s service type
serviceType: ClusterIP
# -- k8s service clusterIP. Only used if serviceType is ClusterIP
clusterIp:
# -- k8s service port
servicePort: 8080
# -- k8s target port
targetPort: 8080
# -- k8s node port. Only used if serviceType is NodePort
nodePort:
# Use Local to preserve the client source IP and avoids a second hop for LoadBalancer and NodePort type services,
# but risks potentially imbalanced traffic spreading.
serviceExternalTrafficPolicy:
# -- Jenkins controller service annotations
serviceAnnotations: {}
# -- Jenkins controller custom labels for the StatefulSet
statefulSetLabels: {}
# foo: bar
# bar: foo
# -- Labels for the Jenkins controller-service
serviceLabels: {}
# service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-backend-protocol: https
# Put labels on Jenkins controller pod
# -- Custom Pod labels (an object with `label-key: label-value` pairs)
podLabels: {}
# Enable Kubernetes Startup, Liveness and Readiness Probes
# if Startup Probe is supported, enable it too
# ~ 2 minutes to allow Jenkins to restart when upgrading plugins. Set ReadinessTimeout to be shorter than LivenessTimeout.
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-liveness-readiness-startup-probes
# -- Enable Kubernetes Probes configuration configured in `controller.probes`
healthProbes: true
probes:
startupProbe:
# -- Set the failure threshold for the startup probe
failureThreshold: 12
httpGet:
# -- Set the Pod's HTTP path for the startup probe
path: '{{ default "" .Values.controller.jenkinsUriPrefix }}/login'
# -- Set the Pod's HTTP port to use for the startup probe
port: http
# -- Set the time interval between two startup probes executions in seconds
periodSeconds: 10
# -- Set the timeout for the startup probe in seconds
timeoutSeconds: 5
livenessProbe:
# -- Set the failure threshold for the liveness probe
failureThreshold: 5
httpGet:
# -- Set the Pod's HTTP path for the liveness probe
path: '{{ default "" .Values.controller.jenkinsUriPrefix }}/login'
# -- Set the Pod's HTTP port to use for the liveness probe
port: http
# -- Set the time interval between two liveness probes executions in seconds
periodSeconds: 10
# -- Set the timeout for the liveness probe in seconds
timeoutSeconds: 5
# If Startup Probe is not supported on your Kubernetes cluster, you might want to use "initialDelaySeconds" instead.
# It delays the initial liveness probe while Jenkins is starting
# -- Set the initial delay for the liveness probe in seconds
initialDelaySeconds:
readinessProbe:
# -- Set the failure threshold for the readiness probe
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
# -- Set the Pod's HTTP path for the liveness probe
path: '{{ default "" .Values.controller.jenkinsUriPrefix }}/login'
# -- Set the Pod's HTTP port to use for the readiness probe
port: http
# -- Set the time interval between two readiness probes executions in seconds
periodSeconds: 10
# -- Set the timeout for the readiness probe in seconds
timeoutSeconds: 5
# If Startup Probe is not supported on your Kubernetes cluster, you might want to use "initialDelaySeconds" instead.
# It delays the initial readiness probe while Jenkins is starting
# -- Set the initial delay for the readiness probe in seconds
initialDelaySeconds:
# PodDisruptionBudget config
podDisruptionBudget:
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/configure-pdb/
# -- Enable Kubernetes Pod Disruption Budget configuration
enabled: false
# For Kubernetes v1.5+, use 'policy/v1beta1'
# For Kubernetes v1.21+, use 'policy/v1'
# -- Policy API version
apiVersion: "policy/v1beta1"
annotations: {}
labels: {}
# -- Number of pods that can be unavailable. Either an absolute number or a percentage
maxUnavailable: "0"
# -- Create Agent listener service
agentListenerEnabled: true
# -- Listening port for agents
agentListenerPort: 50000
# -- Host port to listen for agents
agentListenerHostPort:
# -- Node port to listen for agents
agentListenerNodePort:
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#traffic-policies
# -- Traffic Policy of for the agentListener service
agentListenerExternalTrafficPolicy:
# -- Allowed inbound IP for the agentListener service
agentListenerLoadBalancerSourceRanges:
- 0.0.0.0/0
# -- Disabled agent protocols
disabledAgentProtocols:
- JNLP-connect
- JNLP2-connect
csrf:
defaultCrumbIssuer:
# -- Enable the default CSRF Crumb issuer
enabled: true
# -- Enable proxy compatibility
proxyCompatability: true
# Kubernetes service type for the JNLP agent service
# agentListenerServiceType is the Kubernetes Service type for the JNLP agent service,
# either 'LoadBalancer', 'NodePort', or 'ClusterIP'
# Note if you set this to 'LoadBalancer', you *must* define annotations to secure it. By default,
# this will be an external load balancer and allowing inbound 0.0.0.0/0, a HUGE
# security risk: https://github.com/kubernetes/charts/issues/1341
# -- Defines how to expose the agentListener service
agentListenerServiceType: "ClusterIP"
# -- Annotations for the agentListener service
agentListenerServiceAnnotations: {}
# Optionally, assign an IP to the LoadBalancer agentListenerService LoadBalancer
# GKE users: only regional static IPs will work for Service Load balancer.
# -- Static IP for the agentListener LoadBalancer
agentListenerLoadBalancerIP:
# -- Whether legacy remoting security should be enabled
legacyRemotingSecurityEnabled: false
# Example of a 'LoadBalancer'-type agent listener with annotations securing it
# agentListenerServiceType: LoadBalancer
# agentListenerServiceAnnotations:
# service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-internal: "True"
# service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges: "172.0.0.0/8, 10.0.0.0/8"
# LoadBalancerSourcesRange is a list of allowed CIDR values, which are combined with ServicePort to
# set allowed inbound rules on the security group assigned to the controller load balancer
# -- Allowed inbound IP addresses
loadBalancerSourceRanges:
- 0.0.0.0/0
# -- Optionally assign a known public LB IP
loadBalancerIP:
# Optionally configure a JMX port. This requires additional javaOpts, for example,
# javaOpts: >
# -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=4000
# -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
# -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
# jmxPort: 4000
# -- Open a port, for JMX stats
jmxPort:
# -- Optionally configure other ports to expose in the controller container
extraPorts: []
# - name: BuildInfoProxy
# port: 9000
# targetPort: 9010 (Optional: Use to explicitly set targetPort if different from port)
# Plugins will be installed during Jenkins controller start
# -- List of Jenkins plugins to install. If you don't want to install plugins, set it to `false`
installPlugins:
- kubernetes:4285.v50ed5f624918
- workflow-aggregator:600.vb_57cdd26fdd7
- git:5.4.1
- configuration-as-code:1850.va_a_8c31d3158b_
# If set to false, Jenkins will download the minimum required version of all dependencies.
# -- Download the minimum required version or latest version of all dependencies
installLatestPlugins: true
# -- Set to true to download the latest version of any plugin that is requested to have the latest version
installLatestSpecifiedPlugins: false
# -- List of plugins to install in addition to those listed in controller.installPlugins
additionalPlugins: []
# Without this; whenever the controller gets restarted (Evicted, etc.) it will fetch plugin updates that have the potential to cause breakage.
# Note that for this to work, `persistence.enabled` needs to be set to `true`
# -- Initialize only on first installation. Ensures plugins do not get updated inadvertently. Requires `persistence.enabled` to be set to `true`
initializeOnce: false
# Enable to always override the installed plugins with the values of 'controller.installPlugins' on upgrade or redeployment.
# -- Overwrite installed plugins on start
overwritePlugins: false
# Configures if plugins bundled with `controller.image` should be overwritten with the values of 'controller.installPlugins' on upgrade or redeployment.
# -- Overwrite plugins that are already installed in the controller image
overwritePluginsFromImage: true
# Configures the restrictions for naming projects. Set this key to null or empty to skip it in the default config.
projectNamingStrategy: standard
# Useful with ghprb plugin. The OWASP plugin is not installed by default, please update controller.installPlugins.
# -- Enable HTML parsing using OWASP Markup Formatter Plugin (antisamy-markup-formatter)
enableRawHtmlMarkupFormatter: false
# This is ignored if enableRawHtmlMarkupFormatter is true
# -- Yaml of the markup formatter to use
markupFormatter: plainText
# Used to approve a list of groovy functions in pipelines used the script-security plugin. Can be viewed under /scriptApproval
# -- List of groovy functions to approve
scriptApproval: []
# - "method groovy.json.JsonSlurperClassic parseText java.lang.String"
# - "new groovy.json.JsonSlurperClassic"
# -- Map of groovy init scripts to be executed during Jenkins controller start
initScripts: {}
# test: |-
# print 'adding global pipeline libraries, register properties, bootstrap jobs...'
# -- Name of the existing ConfigMap that contains init scripts
initConfigMap:
# 'name' is a name of an existing secret in the same namespace as jenkins,
# 'keyName' is the name of one of the keys inside the current secret.
# the 'name' and 'keyName' are concatenated with a '-' in between, so for example:
# an existing secret "secret-credentials" and a key inside it named "github-password" should be used in JCasC as ${secret-credentials-github-password}
# 'name' and 'keyName' must be lowercase RFC 1123 label must consist of lower case alphanumeric characters or '-',
# and must start and end with an alphanumeric character (e.g. 'my-name', or '123-abc')
# existingSecret existing secret "secret-credentials" and a key inside it named "github-username" should be used in JCasC as ${github-username}
# When using existingSecret no need to specify the keyName under additionalExistingSecrets.
existingSecret:
# -- List of additional existing secrets to mount
additionalExistingSecrets: []
# ref: https://github.com/jenkinsci/configuration-as-code-plugin/blob/master/docs/features/secrets.adoc#kubernetes-secrets
# additionalExistingSecrets:
# - name: secret-name-1
# keyName: username
# - name: secret-name-1
# keyName: password
# -- List of additional secrets to create and mount
additionalSecrets: []
# ref: https://github.com/jenkinsci/configuration-as-code-plugin/blob/master/docs/features/secrets.adoc#kubernetes-secrets
# additionalSecrets:
# - name: nameOfSecret
# value: secretText
# Generate SecretClaim resources to create Kubernetes secrets from HashiCorp Vault using kube-vault-controller.
# 'name' is the name of the secret that will be created in Kubernetes. The Jenkins fullname is prepended to this value.
# 'path' is the fully qualified path to the secret in Vault
# 'type' is an optional Kubernetes secret type. The default is 'Opaque'
# 'renew' is an optional secret renewal time in seconds
# -- List of `SecretClaim` resources to create
secretClaims: []
# - name: secretName # required
# path: testPath # required
# type: kubernetes.io/tls # optional
# renew: 60 # optional
# -- Name of default cloud configuration.
cloudName: "PangaRabbit K8s"
# Below is the implementation of Jenkins Configuration as Code. Add a key under configScripts for each configuration area,
# where each corresponds to a plugin or section of the UI. Each key (prior to | character) is just a label, and can be any value.
# Keys are only used to give the section a meaningful name. The only restriction is they may only contain RFC 1123 \ DNS label
# characters: lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens. The keys become the name of a configuration yaml file on the controller in
# /var/jenkins_home/casc_configs (by default) and will be processed by the Configuration as Code Plugin. The lines after each |
# become the content of the configuration yaml file. The first line after this is a JCasC root element, e.g., jenkins, credentials,
# etc. Best reference is https://<jenkins_url>/configuration-as-code/reference. The example below creates a welcome message:
JCasC:
# -- Enables default Jenkins configuration via configuration as code plugin
defaultConfig: true
# If true, the init container deletes all the plugin config files and Jenkins Config as Code overwrites any existing configuration
# -- Whether Jenkins Config as Code should overwrite any existing configuration
overwriteConfiguration: false
# -- Remote URLs for configuration files.
configUrls: []
# - https://acme.org/jenkins.yaml
# -- List of Jenkins Config as Code scripts
configScripts: {}
# welcome-message: |
# jenkins:
# systemMessage: Welcome to our CI\CD server. This Jenkins is configured and managed 'as code'.
# Allows adding to the top-level security JCasC section. For legacy purposes, by default, the chart includes apiToken configurations
# -- Jenkins Config as Code security-section
security:
apiToken:
creationOfLegacyTokenEnabled: false
tokenGenerationOnCreationEnabled: false
usageStatisticsEnabled: true
# Ignored if securityRealm is defined in controller.JCasC.configScripts
# -- Jenkins Config as Code Security Realm-section
securityRealm: |-
local:
allowsSignup: false
enableCaptcha: false
users:
- id: "${chart-admin-username}"
name: "Jenkins Admin"
password: "${chart-admin-password}"
# Ignored if authorizationStrategy is defined in controller.JCasC.configScripts
# -- Jenkins Config as Code Authorization Strategy-section
authorizationStrategy: |-
loggedInUsersCanDoAnything:
allowAnonymousRead: false
# -- Annotations for the JCasC ConfigMap
configMapAnnotations: {}
# -- Custom init-container specification in raw-yaml format
customInitContainers: []
# - name: custom-init
# image: "alpine:3"
# imagePullPolicy: Always
# command: [ "uname", "-a" ]
sidecars:
configAutoReload:
# If enabled: true, Jenkins Configuration as Code will be reloaded on-the-fly without a reboot.
# If false or not-specified, JCasC changes will cause a reboot and will only be applied at the subsequent start-up.
# Auto-reload uses the http://<jenkins_url>/reload-configuration-as-code endpoint to reapply config when changes to
# the configScripts are detected.
# -- Enables Jenkins Config as Code auto-reload
enabled: true
image:
# -- Registry for the image that triggers the reload
registry: docker.io
# -- Repository of the image that triggers the reload
repository: kiwigrid/k8s-sidecar
# -- Tag for the image that triggers the reload
tag: 1.27.6
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
{}
# limits:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 100Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 50m
# memory: 50Mi
# -- Enables additional volume mounts for the config auto-reload container
additionalVolumeMounts:
[]
# - name: auto-reload-config
# mountPath: /var/config/logger
# - name: auto-reload-logs
# mountPath: /var/log/auto_reload
# -- Config auto-reload logging settings
logging:
# See default settings https://github.com/kiwigrid/k8s-sidecar/blob/master/src/logger.py
configuration:
# -- Enables custom log config utilizing using the settings below.
override: false
logLevel: INFO
formatter: JSON
logToConsole: true
logToFile: false
maxBytes: 1024
backupCount: 3
# -- The scheme to use when connecting to the Jenkins configuration as code endpoint
scheme: http
# -- Skip TLS verification when connecting to the Jenkins configuration as code endpoint
skipTlsVerify: false
# -- How many connection-related errors to retry on
reqRetryConnect: 10
# -- How many seconds to wait before updating config-maps/secrets (sets METHOD=SLEEP on the sidecar)
sleepTime:
# -- Environment variable sources for the Jenkins Config as Code auto-reload container
envFrom: []
# -- Environment variables for the Jenkins Config as Code auto-reload container
env: {}
# - name: REQ_TIMEOUT
# value: "30"
# SSH port value can be set to any unused TCP port. The default, 1044, is a non-standard SSH port that has been chosen at random.
# This is only used to reload JCasC config from the sidecar container running in the Jenkins controller pod.
# This TCP port will not be open in the pod (unless you specifically configure this), so Jenkins will not be
# accessible via SSH from outside the pod. Note if you use non-root pod privileges (runAsUser & fsGroup),
# this must be > 1024:
sshTcpPort: 1044
# folder in the pod that should hold the collected dashboards:
folder: "/var/jenkins_home/casc_configs"
# If specified, the sidecar will search for JCasC config-maps inside this namespace.
# Otherwise, the namespace in which the sidecar is running will be used.
# It's also possible to specify ALL to search in all namespaces:
# searchNamespace:
# -- Enable container security context
containerSecurityContext:
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
# -- Configures additional sidecar container(s) for the Jenkins controller
additionalSidecarContainers: []
## The example below runs the client for https://smee.io as sidecar container next to Jenkins,
## that allows triggering build behind a secure firewall.
## https://jenkins.io/blog/2019/01/07/webhook-firewalls/#triggering-builds-with-webhooks-behind-a-secure-firewall
##
## Note: To use it you should go to https://smee.io/new and update the url to the generated one.
# - name: smee
# image: docker.io/twalter/smee-client:1.0.2
# args: ["--port", "{{ .Values.controller.servicePort }}", "--path", "/github-webhook/", "--url", "https://smee.io/new"]
# resources:
# limits:
# cpu: 50m
# memory: 128Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
# -- Name of the Kubernetes scheduler to use
schedulerName: ""
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#nodeselector
# -- Node labels for pod assignment
nodeSelector: {}
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#taints-and-tolerations-beta-feature
# -- Toleration labels for pod assignment
tolerations: []
# -- Set TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
terminationGracePeriodSeconds:
# -- Set the termination message path
terminationMessagePath:
# -- Set the termination message policy
terminationMessagePolicy:
# -- Affinity settings
affinity: {}
# Leverage a priorityClass to ensure your pods survive resource shortages
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/pod-priority-preemption/
# -- The name of a `priorityClass` to apply to the controller pod
priorityClassName:
# -- Annotations for controller pod
podAnnotations: {}
# -- Annotations for controller StatefulSet
statefulSetAnnotations: {}
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/statefulset/#update-strategies
# -- Update strategy for StatefulSet
updateStrategy: {}
# -- Topology spread constraints
topologySpreadConstraints: {}
ingress:
# -- Enables ingress
enabled: true
# Override for the default paths that map requests to the backend
# -- Override for the default Ingress paths
paths: []
# - backend:
# serviceName: ssl-redirect
# servicePort: use-annotation
# - backend:
# serviceName: >-
# {{ template "jenkins.fullname" . }}
# # Don't use string here, use only integer value!
# servicePort: 8080
# For Kubernetes v1.14+, use 'networking.k8s.io/v1beta1'
# For Kubernetes v1.19+, use 'networking.k8s.io/v1'
# -- Ingress API version
apiVersion: "extensions/v1beta1"
# -- Ingress labels
labels: {}
# -- Ingress annotations
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: traefik
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
# For Kubernetes >= 1.18 you should specify the ingress-controller via the field ingressClassName
# See https://kubernetes.io/blog/2020/04/02/improvements-to-the-ingress-api-in-kubernetes-1.18/#specifying-the-class-of-an-ingress
# ingressClassName: nginx
# Set this path to jenkinsUriPrefix above or use annotations to rewrite path
# -- Ingress path
path:
# configures the hostname e.g. jenkins.example.com
# -- Ingress hostname
hostName: jenkins.pangarabbit.com
# -- Hostname to serve assets from
resourceRootUrl:
# -- Ingress TLS configuration
tls: []
# - secretName: jenkins.cluster.local
# hosts:
# - jenkins.cluster.local
# often you want to have your controller all locked down and private,
# but you still want to get webhooks from your SCM
# A secondary ingress will let you expose different urls
# with a different configuration
secondaryingress:
enabled: false
# paths you want forwarded to the backend
# ex /github-webhook
paths: []
# For Kubernetes v1.14+, use 'networking.k8s.io/v1beta1'
# For Kubernetes v1.19+, use 'networking.k8s.io/v1'
apiVersion: "extensions/v1beta1"
labels: {}
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: traefik
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
# For Kubernetes >= 1.18 you should specify the ingress-controller via the field ingressClassName
# See https://kubernetes.io/blog/2020/04/02/improvements-to-the-ingress-api-in-kubernetes-1.18/#specifying-the-class-of-an-ingress
# ingressClassName: nginx
# configures the hostname e.g., jenkins-external.example.com
hostName:
tls:
# - secretName: jenkins-external.example.com
# hosts:
# - jenkins-external.example.com
# If you're running on GKE and need to configure a backendconfig
# to finish ingress setup, use the following values.
# Docs: https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/concepts/backendconfig
backendconfig:
# -- Enables backendconfig
enabled: false
# -- backendconfig API version
apiVersion: "extensions/v1beta1"
# -- backendconfig name
name:
# -- backendconfig labels
labels: {}
# -- backendconfig annotations
annotations: {}
# -- backendconfig spec
spec: {}
# Openshift route
route:
# -- Enables openshift route
enabled: false
# -- Route labels
labels: {}
# -- Route annotations
annotations: {}
# -- Route path
path:
# -- Allows for adding entries to Pod /etc/hosts
hostAliases: []
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/add-entries-to-pod-etc-hosts-with-host-aliases/
# hostAliases:
# - ip: 192.168.50.50
# hostnames:
# - something.local
# - ip: 10.0.50.50
# hostnames:
# - other.local
# Expose Prometheus metrics
prometheus:
# If enabled, add the prometheus plugin to the list of plugins to install
# https://plugins.jenkins.io/prometheus
# -- Enables prometheus service monitor
enabled: false
# -- Additional labels to add to the service monitor object
serviceMonitorAdditionalLabels: {}
# -- Set a custom namespace where to deploy ServiceMonitor resource
serviceMonitorNamespace:
# -- How often prometheus should scrape metrics
scrapeInterval: 60s
# Defaults to the default endpoint used by the prometheus plugin
# -- The endpoint prometheus should get metrics from
scrapeEndpoint: /prometheus
# See here: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/alerting_rules/
# The `groups` root object is added by default, add the rule entries
# -- Array of prometheus alerting rules
alertingrules: []
# -- Additional labels to add to the PrometheusRule object
alertingRulesAdditionalLabels: {}
# -- Set a custom namespace where to deploy PrometheusRule resource
prometheusRuleNamespace: ""
# RelabelConfigs to apply to samples before scraping. Prometheus Operator automatically adds
# relabelings for a few standard Kubernetes fields. The original scrape job’s name
# is available via the __tmp_prometheus_job_name label.
# More info: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#relabel_config
relabelings: []
# MetricRelabelConfigs to apply to samples before ingestion.
metricRelabelings: []
googlePodMonitor:
# If enabled, It creates Google Managed Prometheus scraping config
enabled: false
# Set a custom namespace where to deploy PodMonitoring resource
# serviceMonitorNamespace: ""
scrapeInterval: 60s
# This is the default endpoint used by the prometheus plugin
scrapeEndpoint: /prometheus
# -- Can be used to disable rendering controller test resources when using helm template
testEnabled: true
httpsKeyStore:
# -- Enables HTTPS keystore on jenkins controller
enable: false
# -- Name of the secret that already has ssl keystore
jenkinsHttpsJksSecretName: ""
# -- Name of the key in the secret that already has ssl keystore
jenkinsHttpsJksSecretKey: "jenkins-jks-file"
# -- Name of the secret that contains the JKS password, if it is not in the same secret as the JKS file
jenkinsHttpsJksPasswordSecretName: ""
# -- Name of the key in the secret that contains the JKS password
jenkinsHttpsJksPasswordSecretKey: "https-jks-password"
disableSecretMount: false
# When HTTPS keystore is enabled, servicePort and targetPort will be used as HTTPS port
# -- HTTP Port that Jenkins should listen to along with HTTPS, it also serves as the liveness and readiness probes port.
httpPort: 8081
# -- Path of HTTPS keystore file
path: "/var/jenkins_keystore"
# -- Jenkins keystore filename which will appear under controller.httpsKeyStore.path
fileName: "keystore.jks"
# -- Jenkins keystore password
password: "password"
# -- Base64 encoded Keystore content. Keystore must be converted to base64 then being pasted here
jenkinsKeyStoreBase64Encoded:
# Convert keystore.jks files content to base64 > $ cat keystore.jks | base64
# /u3+7QAAAAIAAAABAAAAAQANamVua2luc2NpLmNvbQAAAW2r/b1ZAAAFATCCBP0wDgYKKwYBBAEq
# AhEBAQUABIIE6QbCqasvoHS0pSwYqSvdydMCB9t+VNfwhFIiiuAelJfO5sSe2SebJbtwHgLcRz1Z
# gMtWgOSFdl3bWSzA7vrW2LED52h+jXLYSWvZzuDuh8hYO85m10ikF6QR+dTi4jra0whIFDvq3pxe
# TnESxEsN+DvbZM3jA3qsjQJSeISNpDjO099dqQvHpnCn18lyk7J4TWJ8sOQQb1EM2zDAfAOSqA/x
# QuPEFl74DlY+5DIk6EBvpmWhaMSvXzWZACGA0sYqa157dq7O0AqmuLG/EI5EkHETO4CrtBW+yLcy
# 2dUCXOMA+j+NjM1BjrQkYE5vtSfNO6lFZcISyKo5pTFlcA7ut0Fx2nZ8GhHTn32CpeWwNcZBn1gR
# pZVt6DxVVkhTAkMLhR4rL2wGIi/1WRs23ZOLGKtyDNvDHnQyDiQEoJGy9nAthA8aNHa3cfdF10vB
# Drb19vtpFHmpvKEEhpk2EBRF4fTi644Fuhu2Ied6118AlaPvEea+n6G4vBz+8RWuVCmZjLU+7h8l
# Hy3/WdUPoIL5eW7Kz+hS+sRTFzfu9C48dMkQH3a6f3wSY+mufizNF9U298r98TnYy+PfDJK0bstG
# Ph6yPWx8DGXKQBwrhWJWXI6JwZDeC5Ny+l8p1SypTmAjpIaSW3ge+KgcL6Wtt1R5hUV1ajVwVSUi
# HF/FachKqPqyLJFZTGjNrxnmNYpt8P1d5JTvJfmfr55Su/P9n7kcyWp7zMcb2Q5nlXt4tWogOHLI
# OzEWKCacbFfVHE+PpdrcvCVZMDzFogIq5EqGTOZe2poPpBVE+1y9mf5+TXBegy5HToLWvmfmJNTO
# NCDuBjgLs2tdw2yMPm4YEr57PnMX5gGTC3f2ZihXCIJDCRCdQ9sVBOjIQbOCzxFXkVITo0BAZhCi
# Yz61wt3Ud8e//zhXWCkCsSV+IZCxxPzhEFd+RFVjW0Nm9hsb2FgAhkXCjsGROgoleYgaZJWvQaAg
# UyBzMmKDPKTllBHyE3Gy1ehBNGPgEBChf17/9M+j8pcm1OmlM434ctWQ4qW7RU56//yq1soFY0Te
# fu2ei03a6m68fYuW6s7XEEK58QisJWRAvEbpwu/eyqfs7PsQ+zSgJHyk2rO95IxdMtEESb2GRuoi
# Bs+AHNdYFTAi+GBWw9dvEgqQ0Mpv0//6bBE/Fb4d7b7f56uUNnnE7mFnjGmGQN+MvC62pfwfvJTT
# EkT1iZ9kjM9FprTFWXT4UmO3XTvesGeE50sV9YPm71X4DCQwc4KE8vyuwj0s6oMNAUACW2ClU9QQ
# y0tRpaF1tzs4N42Q5zl0TzWxbCCjAtC3u6xf+c8MCGrr7DzNhm42LOQiHTa4MwX4x96q7235oiAU
# iQqSI/hyF5yLpWw4etyUvsx2/0/0wkuTU1FozbLoCWJEWcPS7QadMrRRISxHf0YobIeQyz34regl
# t1qSQ3dCU9D6AHLgX6kqllx4X0fnFq7LtfN7fA2itW26v+kAT2QFZ3qZhINGfofCja/pITC1uNAZ
# gsJaTMcQ600krj/ynoxnjT+n1gmeqThac6/Mi3YlVeRtaxI2InL82ZuD+w/dfY9OpPssQjy3xiQa
# jPuaMWXRxz/sS9syOoGVH7XBwKrWpQcpchozWJt40QV5DslJkclcr8aC2AGlzuJMTdEgz1eqV0+H
# bAXG9HRHN/0eJTn1/QAAAAEABVguNTA5AAADjzCCA4swggJzAhRGqVxH4HTLYPGO4rzHcCPeGDKn
# xTANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADCBgTELMAkGA1UEBhMCY2ExEDAOBgNVBAgMB29udGFyaW8xEDAOBgNV
# BAcMB3Rvcm9udG8xFDASBgNVBAoMC2plbmtpbnN0ZXN0MRkwFwYDVQQDDBBqZW5raW5zdGVzdC5p
# bmZvMR0wGwYJKoZIhvcNAQkBFg50ZXN0QHRlc3QuaW5mbzAeFw0xOTEwMDgxNTI5NTVaFw0xOTEx
# MDcxNTI5NTVaMIGBMQswCQYDVQQGEwJjYTEQMA4GA1UECAwHb250YXJpbzEQMA4GA1UEBwwHdG9y
# b250bzEUMBIGA1UECgwLamVua2luc3Rlc3QxGTAXBgNVBAMMEGplbmtpbnN0ZXN0LmluZm8xHTAb
# BgkqhkiG9w0BCQEWDnRlc3RAdGVzdC5pbmZvMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKC
# AQEA02q352JTHGvROMBhSHvSv+vnoOTDKSTz2aLQn0tYrIRqRo+8bfmMjXuhkwZPSnCpvUGNAJ+w
# Jrt/dqMoYUjCBkjylD/qHmnXN5EwS1cMg1Djh65gi5JJLFJ7eNcoSsr/0AJ+TweIal1jJSP3t3PF
# 9Uv21gm6xdm7HnNK66WpUUXLDTKaIs/jtagVY1bLOo9oEVeLN4nT2CYWztpMvdCyEDUzgEdDbmrP
# F5nKUPK5hrFqo1Dc5rUI4ZshL3Lpv398aMxv6n2adQvuL++URMEbXXBhxOrT6rCtYzbcR5fkwS9i
# d3Br45CoWOQro02JAepoU0MQKY5+xQ4Bq9Q7tB9BAwIDAQABMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAA4IBAQAe
# 4xc+mSvKkrKBHg9/zpkWgZUiOp4ENJCi8H4tea/PCM439v6y/kfjT/okOokFvX8N5aa1OSz2Vsrl
# m8kjIc6hiA7bKzT6lb0EyjUShFFZ5jmGVP4S7/hviDvgB5yEQxOPpumkdRP513YnEGj/o9Pazi5h
# /MwpRxxazoda9r45kqQpyG+XoM4pB+Fd3JzMc4FUGxfVPxJU4jLawnJJiZ3vqiSyaB0YyUL+Er1Q
# 6NnqtR4gEBF0ZVlQmkycFvD4EC2boP943dLqNUvop+4R3SM1QMM6P5u8iTXtHd/VN4MwMyy1wtog
# hYAzODo1Jt59pcqqKJEas0C/lFJEB3frw4ImNx5fNlJYOpx+ijfQs9m39CevDq0=
agent:
# -- Enable Kubernetes plugin jnlp-agent podTemplate
enabled: true
# -- The name of the pod template to use for providing default values
defaultsProviderTemplate: ""
# Useful for not including a serviceAccount in the template if `false`
# -- Use `serviceAccountAgent.name` as the default value for defaults template `serviceAccount`
useDefaultServiceAccount: true
# -- Override the default service account
# @default -- `serviceAccountAgent.name` if `agent.useDefaultServiceAccount` is `true`
serviceAccount:
# For connecting to the Jenkins controller
# -- Overrides the Kubernetes Jenkins URL
jenkinsUrl:
# connects to the specified host and port, instead of connecting directly to the Jenkins controller
# -- Overrides the Kubernetes Jenkins tunnel
jenkinsTunnel:
# -- Disables the verification of the controller certificate on remote connection. This flag correspond to the "Disable https certificate check" flag in kubernetes plugin UI
skipTlsVerify: false
# -- Enable the possibility to restrict the usage of this agent to specific folder. This flag correspond to the "Restrict pipeline support to authorized folders" flag in kubernetes plugin UI
usageRestricted: false
# -- The connection timeout in seconds for connections to Kubernetes API. The minimum value is 5
kubernetesConnectTimeout: 5
# -- The read timeout in seconds for connections to Kubernetes API. The minimum value is 15
kubernetesReadTimeout: 15
# -- The maximum concurrent connections to Kubernetes API
maxRequestsPerHostStr: "32"
# -- Time in minutes after which the Kubernetes cloud plugin will clean up an idle worker that has not already terminated
retentionTimeout: 5
# -- Seconds to wait for pod to be running
waitForPodSec: 600
# -- Namespace in which the Kubernetes agents should be launched
namespace:
# -- Custom Pod labels (an object with `label-key: label-value` pairs)
podLabels: {}
# -- Custom registry used to pull the agent jnlp image from
jnlpregistry:
image:
# -- Repository to pull the agent jnlp image from
repository: "jenkins/inbound-agent"
# -- Tag of the image to pull
tag: "3261.v9c670a_4748a_9-1"
# -- Configure working directory for default agent
workingDir: "/home/jenkins/agent"
nodeUsageMode: "NORMAL"
# -- Append Jenkins labels to the agent
customJenkinsLabels: []
# -- Name of the secret to be used to pull the image
imagePullSecretName:
componentName: "jenkins-agent"
# -- Enables agent communication via websockets
websocket: false
directConnection: false
# -- Agent privileged container
privileged: false
# -- Configure container user
runAsUser:
# -- Configure container group
runAsGroup:
# -- Enables the agent to use the host network
hostNetworking: false
# -- Resources allocation (Requests and Limits)
resources:
requests:
cpu: "512m"
memory: "512Mi"
# ephemeralStorage:
limits:
cpu: "512m"
memory: "512Mi"
# ephemeralStorage:
livenessProbe: {}
# execArgs: "cat /tmp/healthy"
# failureThreshold: 3
# initialDelaySeconds: 0
# periodSeconds: 10
# successThreshold: 1
# timeoutSeconds: 1
# You may want to change this to true while testing a new image
# -- Always pull agent container image before build
alwaysPullImage: false
# When using Pod Security Admission in the Agents namespace with the restricted Pod Security Standard,
# the jnlp container cannot be scheduled without overriding its container definition with a securityContext.
# This option allows to automatically inject in the jnlp container a securityContext
# that is suitable for the use of the restricted Pod Security Standard.
# -- Set a restricted securityContext on jnlp containers
restrictedPssSecurityContext: false
# Controls how agent pods are retained after the Jenkins build completes
# Possible values: Always, Never, OnFailure
podRetention: "Never"
# Disable if you do not want the Yaml the agent pod template to show up
# in the job Console Output. This can be helpful for either security reasons
# or simply to clean up the output to make it easier to read.
showRawYaml: true
# You can define the volumes that you want to mount for this container
# Allowed types are: ConfigMap, EmptyDir, EphemeralVolume, HostPath, Nfs, PVC, Secret
# Configure the attributes as they appear in the corresponding Java class for that type
# https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-plugin/tree/master/src/main/java/org/csanchez/jenkins/plugins/kubernetes/volumes
# -- Additional volumes
volumes: []
# - type: ConfigMap
# configMapName: myconfigmap
# mountPath: /var/myapp/myconfigmap
# - type: EmptyDir
# mountPath: /var/myapp/myemptydir
# memory: false
# - type: EphemeralVolume
# mountPath: /var/myapp/myephemeralvolume
# accessModes: ReadWriteOnce
# requestsSize: 10Gi
# storageClassName: mystorageclass
# - type: HostPath
# hostPath: /var/lib/containers
# mountPath: /var/myapp/myhostpath
# - type: Nfs
# mountPath: /var/myapp/mynfs
# readOnly: false
# serverAddress: "192.0.2.0"
# serverPath: /var/lib/containers
# - type: PVC
# claimName: mypvc
# mountPath: /var/myapp/mypvc
# readOnly: false
# - type: Secret
# defaultMode: "600"
# mountPath: /var/myapp/mysecret
# secretName: mysecret
# Pod-wide environment, these vars are visible to any container in the agent pod
# You can define the workspaceVolume that you want to mount for this container
# Allowed types are: DynamicPVC, EmptyDir, EphemeralVolume, HostPath, Nfs, PVC
# Configure the attributes as they appear in the corresponding Java class for that type
# https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-plugin/tree/master/src/main/java/org/csanchez/jenkins/plugins/kubernetes/volumes/workspace
# -- Workspace volume (defaults to EmptyDir)
workspaceVolume: {}
## DynamicPVC example
# - type: DynamicPVC
# configMapName: myconfigmap
## EmptyDir example
# - type: EmptyDir
# memory: false
## EphemeralVolume example
# - type: EphemeralVolume
# accessModes: ReadWriteOnce
# requestsSize: 10Gi
# storageClassName: mystorageclass
## HostPath example
# - type: HostPath
# hostPath: /var/lib/containers
## NFS example
# - type: Nfs
# readOnly: false
# serverAddress: "192.0.2.0"
# serverPath: /var/lib/containers
## PVC example
# - type: PVC
# claimName: mypvc
# readOnly: false
# Pod-wide environment, these vars are visible to any container in the agent pod
# -- Environment variables for the agent Pod
envVars: []
# - name: PATH
# value: /usr/local/bin
# -- Mount a secret as environment variable
secretEnvVars: []
# - key: PATH
# optional: false # default: false
# secretKey: MY-K8S-PATH
# secretName: my-k8s-secret
# -- Node labels for pod assignment
nodeSelector: {}
# Key Value selectors. Ex:
# nodeSelector
# jenkins-agent: v1
# -- Command to execute when side container starts
command:
# -- Arguments passed to command to execute
args: "${computer.jnlpmac} ${computer.name}"
# -- Side container name
sideContainerName: "jnlp"
# Doesn't allocate pseudo TTY by default
# -- Allocate pseudo tty to the side container
TTYEnabled: false
# -- Max number of agents to launch
containerCap: 10
# -- Agent Pod base name
podName: "default"
# Enables garbage collection of orphan pods for this Kubernetes cloud. (beta)
garbageCollection:
# -- When enabled, Jenkins will periodically check for orphan pods that have not been touched for the given timeout period and delete them.
enabled: false
# -- Namespaces to look at for garbage collection, in addition to the default namespace defined for the cloud. One namespace per line.
namespaces: ""
# namespaces: |-
# namespaceOne
# namespaceTwo
# -- Timeout value for orphaned pods
timeout: 300
# -- Allows the Pod to remain active for reuse until the configured number of minutes has passed since the last step was executed on it
idleMinutes: 0
# The raw yaml of a Pod API Object, for example, this allows usage of toleration for agent pods.
# https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-plugin#using-yaml-to-define-pod-templates
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/
# -- The raw yaml of a Pod API Object to merge into the agent spec
yamlTemplate: ""
# yamlTemplate: |-
# apiVersion: v1
# kind: Pod
# spec:
# tolerations:
# - key: "key"
# operator: "Equal"
# value: "value"
# -- Defines how the raw yaml field gets merged with yaml definitions from inherited pod templates. Possible values: "merge" or "override"
yamlMergeStrategy: "override"
# -- Controls whether the defined yaml merge strategy will be inherited if another defined pod template is configured to inherit from the current one
inheritYamlMergeStrategy: false
# -- Timeout in seconds for an agent to be online
connectTimeout: 100
# -- Annotations to apply to the pod
annotations: {}
# Containers specified here are added to all agents. Set key empty to remove container from additional agents.
# -- Add additional containers to the agents
additionalContainers: []
# - sideContainerName: dind
# image:
# repository: docker
# tag: dind
# command: dockerd-entrypoint.sh
# args: ""
# privileged: true
# resources:
# requests:
# cpu: 500m
# memory: 1Gi
# limits:
# cpu: 1
# memory: 2Gi
# Useful when configuring agents only with the podTemplates value, since the default podTemplate populated by values mentioned above will be excluded in the rendered template.
# -- Disable the default Jenkins Agent configuration
disableDefaultAgent: false
# Below is the implementation of custom pod templates for the default configured kubernetes cloud.
# Add a key under podTemplates for each pod template. Each key (prior to | character) is just a label, and can be any value.
# Keys are only used to give the pod template a meaningful name. The only restriction is they may only contain RFC 1123 \ DNS label
# characters: lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens. Each pod template can contain multiple containers.
# For this pod templates configuration to be loaded, the following values must be set:
# controller.JCasC.defaultConfig: true
# Best reference is https://<jenkins_url>/configuration-as-code/reference#Cloud-kubernetes. The example below creates a python pod template.
# -- Configures extra pod templates for the default kubernetes cloud
podTemplates:
python2-template: |
- name: python2-template
label: python2-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: python
image: python:2
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
python3-template: |
- name: python3-template
label: python3-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: python
image: python:3
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
mavenjdk8-template: |
- name: mavenjdk8-template
label: mavenjdk8-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: maven
image: maven:latest
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
mavenjdk11-template: |
- name: mavenjdk11-template
label: mavenjdk11-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: maven
image: maven:jdk11
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
mavenjdk17-template: |
- name: mavenjdk17-template
label: mavenjdk17-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: maven
image: maven:jdk17
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
mavenjdk21-template: |
- name: mavenjdk21-template
label: mavenjdk21-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: maven
image: maven:jdk21
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
# Inherits all values from `agent` so you only need to specify values which differ
# -- Configure additional
additionalAgents:
mavenjdk8:
podName: mavenjdk8
customJenkinsLabels: mavenjdk8
sideContainerName: mavenjdk8
image:
repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest
mavenjdk11:
podName: mavenjdk11
customJenkinsLabels: mavenjdk11
sideContainerName: mavenjdk11
image:
repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest-jdk11
mavenjdk17:
podName: mavenjdk17
customJenkinsLabels: mavenjdk17
sideContainerName: mavenjdk17
image:
repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest-jdk17
mavenjdk21:
podName: mavenjdk21
customJenkinsLabels: mavenjdk21
sideContainerName: mavenjdk21
image:
repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest-jdk21
python2:
podName: python2
customJenkinsLabels: python2
sideContainerName: python2
image:
repository: python
tag: "2"
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
TTYEnabled: true
python3:
podName: python3
customJenkinsLabels: python3
sideContainerName: python3
image:
repository: python
tag: "3"
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
TTYEnabled: true
# Here you can add additional clouds
# They inherit all values from the default cloud (including the main agent), so
# you only need to specify values which differ. If you want to override
# default additionalAgents with the additionalClouds.additionalAgents set
# additionalAgentsOverride to `true`.
additionalClouds: {}
# remote-cloud-1:
# kubernetesURL: https://api.remote-cloud.com
# additionalAgentsOverride: true
# additionalAgents:
# maven-2:
# podName: maven-2
# customJenkinsLabels: maven
# # An example of overriding the jnlp container
# # sideContainerName: jnlp
# image:
# repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
# tag: latest
# namespace: my-other-maven-namespace
# remote-cloud-2:
# kubernetesURL: https://api.remote-cloud.com
persistence:
# -- Enable the use of a Jenkins PVC
enabled: true
# A manually managed Persistent Volume and Claim
# Requires persistence.enabled: true
# If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
# -- Provide the name of a PVC
existingClaim:
# jenkins data Persistent Volume Storage Class
# If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
# If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
# If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
# set, choosing the default provisioner (gp2 on AWS, standard on GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
# -- Storage class for the PVC
storageClass: nfs-csi-jenkins # Replace with your storage class
# -- Annotations for the PVC
annotations: {}
# -- Labels for the PVC
labels: {}
# -- The PVC access mode
accessMode: "ReadWriteOnce"
# -- The size of the PVC
size: "8Gi"
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volume-pvc-datasource/
# -- Existing data source to clone PVC from
dataSource: {}
# name: PVC-NAME
# kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
# -- SubPath for jenkins-home mount
subPath:
# -- Additional volumes
volumes: []
# - name: nothing
# emptyDir: {}
# -- Additional mounts
mounts: []
# - mountPath: /var/nothing
# name: nothing
# readOnly: true
networkPolicy:
# -- Enable the creation of NetworkPolicy resources
enabled: false
# For Kubernetes v1.4, v1.5 and v1.6, use 'extensions/v1beta1'
# For Kubernetes v1.7, use 'networking.k8s.io/v1'
# -- NetworkPolicy ApiVersion
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
# You can allow agents to connect from both within the cluster (from within specific/all namespaces) AND/OR from a given external IP range
internalAgents:
# -- Allow internal agents (from the same cluster) to connect to controller. Agent pods will be filtered based on PodLabels
allowed: true
# -- A map of labels (keys/values) that agent pods must have to be able to connect to controller
podLabels: {}
# -- A map of labels (keys/values) that agents namespaces must have to be able to connect to controller
namespaceLabels:
{}
# project: myproject
externalAgents:
# -- The IP range from which external agents are allowed to connect to controller, i.e., 172.17.0.0/16
ipCIDR:
# -- A list of IP sub-ranges to be excluded from the allowlisted IP range
except:
[]
# - 172.17.1.0/24
## Install Default RBAC roles and bindings
rbac:
# -- Whether RBAC resources are created
create: true
# -- Whether the Jenkins service account should be able to read Kubernetes secrets
readSecrets: false
serviceAccount:
# -- Configures if a ServiceAccount with this name should be created
create: true
# The name of the ServiceAccount is autogenerated by default
# -- The name of the ServiceAccount to be used by access-controlled resources
name:
# -- Configures annotations for the ServiceAccount
annotations: {}
# -- Configures extra labels for the ServiceAccount
extraLabels: {}
# -- Controller ServiceAccount image pull secret
imagePullSecretName:
serviceAccountAgent:
# -- Configures if an agent ServiceAccount should be created
create: false
# If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
# -- The name of the agent ServiceAccount to be used by access-controlled resources
name:
# -- Configures annotations for the agent ServiceAccount
annotations: {}
# -- Configures extra labels for the agent ServiceAccount
extraLabels: {}
# -- Agent ServiceAccount image pull secret
imagePullSecretName:
# -- Checks if any deprecated values are used
checkDeprecation: true
awsSecurityGroupPolicies:
enabled: false
policies:
- name: ""
securityGroupIds: []
podSelector: {}
# Here you can configure unit tests values when executing the helm unittest in the CONTRIBUTING.md
helmtest:
# A testing framework for bash
bats:
# Bash Automated Testing System (BATS)
image:
# -- Registry of the image used to test the framework
registry: "docker.io"
# -- Repository of the image used to test the framework
repository: "bats/bats"
# -- Tag of the image to test the framework
tag: "1.11.0"
- Lets git it
git add .
git commit -m "deploy jenkins"
git push
Fluxcd is doing the following under the hood | Jenkins
- Helm repo add
helm repo add jenkins https://charts.jenkins.io --force-update
- Helm install Jenkins
helm install [RELEASE_NAME] jenkins/jenkins [flags]
Kubernetes check | Jenkins
- Kubectl switch to the infrastructure namespace
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=infrastructure
- Kubectl show me the pod for Jenkins
kubectl get pods -n infrastructure | grep jenkins

If everything went well you should be able to access the Jenkins frontend with your domain name for example mine is
https://jenkins.pangarabbit.com
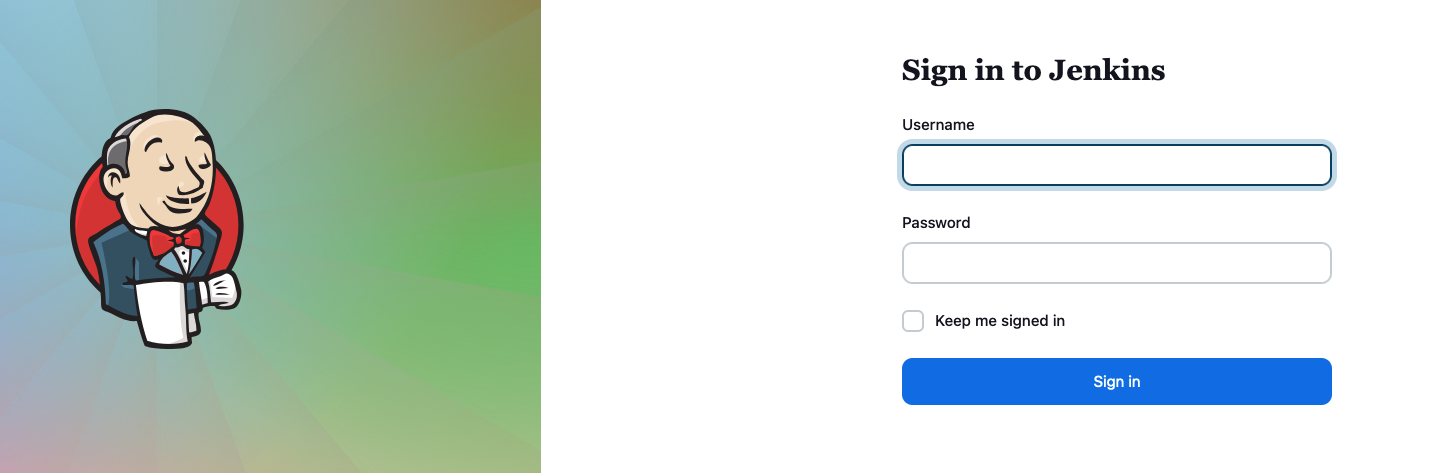
How do we login?
- By default the username is
adminand the password is base64 encoded. - Open your terminal and run the following command but make sure you have switched to the
infrastructurenamespace first.
# Switch to the infrastructure namespace
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=infrastructure
# Get the Jenkins admin password
jsonpath="{.data.jenkins-admin-password}"
kubectl get secret jenkins -o jsonpath=$jsonpath
- You should get a string similar to this fictious example generated by ChatGPT
U29mdHdhcmUgbGVhcm5pbmcgaXMgdGhlIGZ1dHVyZSBvZiB0ZWNobm9sb2d5IQ==
- Head over to this URL to decode the base64 string to reveal your password and login.
Jenkins admin password change
- Click
Jenkins Admindrop down in the top right hand corner of the GUI

- Click
Configure
- Scroll down until you see the
Passwordsection
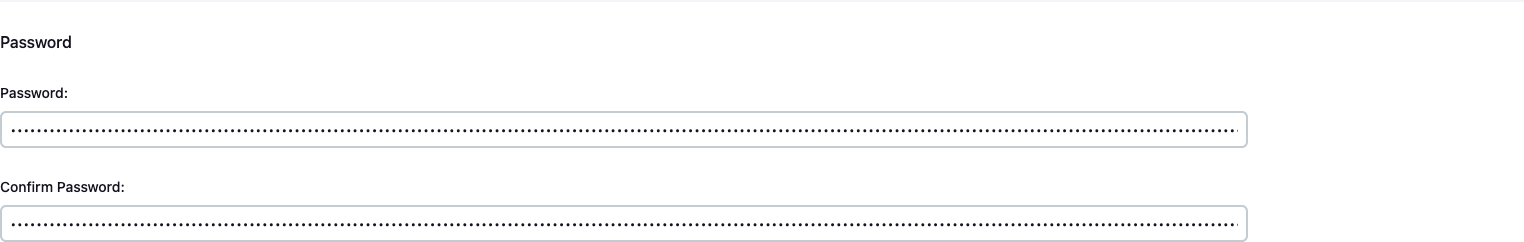
- Change your password and
Save
Jenkins GitHub Setup
- Click
Manage Jenkinsin the left hand menu

- Click
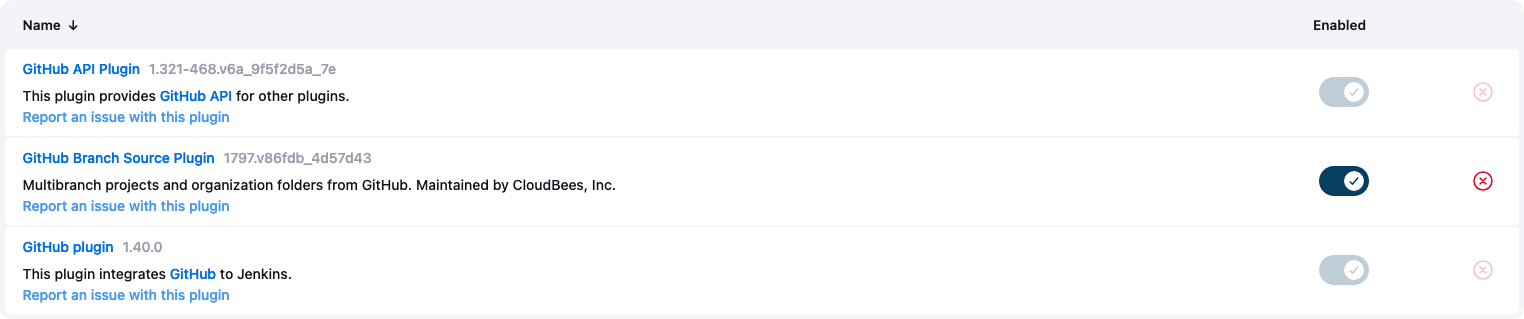
Plugins

- Check that you see the following Plugins installed if not install
GitHub API Plugin,GitHub Branch Source Plugin,GitHub Plugin
- Go to GitHub and create a repository called
ortelius-jenkins-demo-app - Now we need to create a PAT (personal access token) for Jenkins to use to access your repos
- Click on your profile in the top right hand corner of the browser and select
settings
- Scroll down a bit and click on
Developer Settings

- Drop down
Personal Access Tokens

- Click on
Tokens (classic)

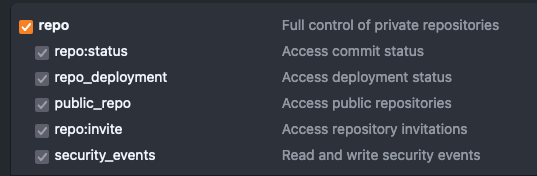
- Give it a meaningful name and assign the following permissions
- Record the key safely in a password manager such as Bitwarden as you will only get one chance to do so
- Go back to Jenkins to add the PAT to your Jenkins credentials
- Click on
Manage Jenkins

- Click on
Credentials

- Select
Global credentialsand click onAdd Credentials
- Select
Dashboardin the top left of your browser

Jenkins Agent Setup
Agents and agent templates are managed inside your Helm Chart. If you add them through the Jenkins GUI Fluxcd will reconcile the configuration in your Helm Chart and your config will vanish so thats why we store our config in our Helm Chart which honours the GitOps methodology where your repo is the source of truth. You will see this happening in Gimlet under Helm Releases.
# Below is the implementation of custom pod templates for the default configured kubernetes cloud.
# Add a key under podTemplates for each pod template. Each key (prior to | character) is just a label, and can be any value.
# Keys are only used to give the pod template a meaningful name. The only restriction is they may only contain RFC 1123 \ DNS label
# characters: lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens. Each pod template can contain multiple containers.
# For this pod templates configuration to be loaded, the following values must be set:
# controller.JCasC.defaultConfig: true
# Best reference is https://<jenkins_url>/configuration-as-code/reference#Cloud-kubernetes. The example below creates a python pod template.
# -- Configures extra pod templates for the default kubernetes cloud
podTemplates:
python2-template: |
- name: python2-template
label: python2-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: python
image: python:2
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
python3-template: |
- name: python3-template
label: python3-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: python
image: python:3
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
mavenjdk8-template: |
- name: mavenjdk8-template
label: mavenjdk8-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: maven
image: maven:latest
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
mavenjdk11-template: |
- name: mavenjdk11-template
label: mavenjdk11-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: maven
image: maven:jdk11
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
mavenjdk17-template: |
- name: mavenjdk17-template
label: mavenjdk17-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: maven
image: maven:jdk17
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
mavenjdk21-template: |
- name: mavenjdk21-template
label: mavenjdk21-template
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: maven
image: maven:jdk21
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
# Inherits all values from `agent` so you only need to specify values which differ
# -- Configure additional
additionalAgents:
mavenjdk8:
podName: mavenjdk8
customJenkinsLabels: mavenjdk8
sideContainerName: mavenjdk8
image:
repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest
mavenjdk11:
podName: mavenjdk11
customJenkinsLabels: mavenjdk11
sideContainerName: mavenjdk11
image:
repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest-jdk11
mavenjdk17:
podName: mavenjdk17
customJenkinsLabels: mavenjdk17
sideContainerName: mavenjdk17
image:
repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest-jdk17
mavenjdk21:
podName: mavenjdk21
customJenkinsLabels: mavenjdk21
sideContainerName: mavenjdk21
image:
repository: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest-jdk21
python2:
podName: python2
customJenkinsLabels: python2
sideContainerName: python2
image:
repository: python
tag: "2"
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
TTYEnabled: true
python3:
podName: python3
customJenkinsLabels: python3
sideContainerName: python3
image:
repository: python
tag: "3"
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
TTYEnabled: true
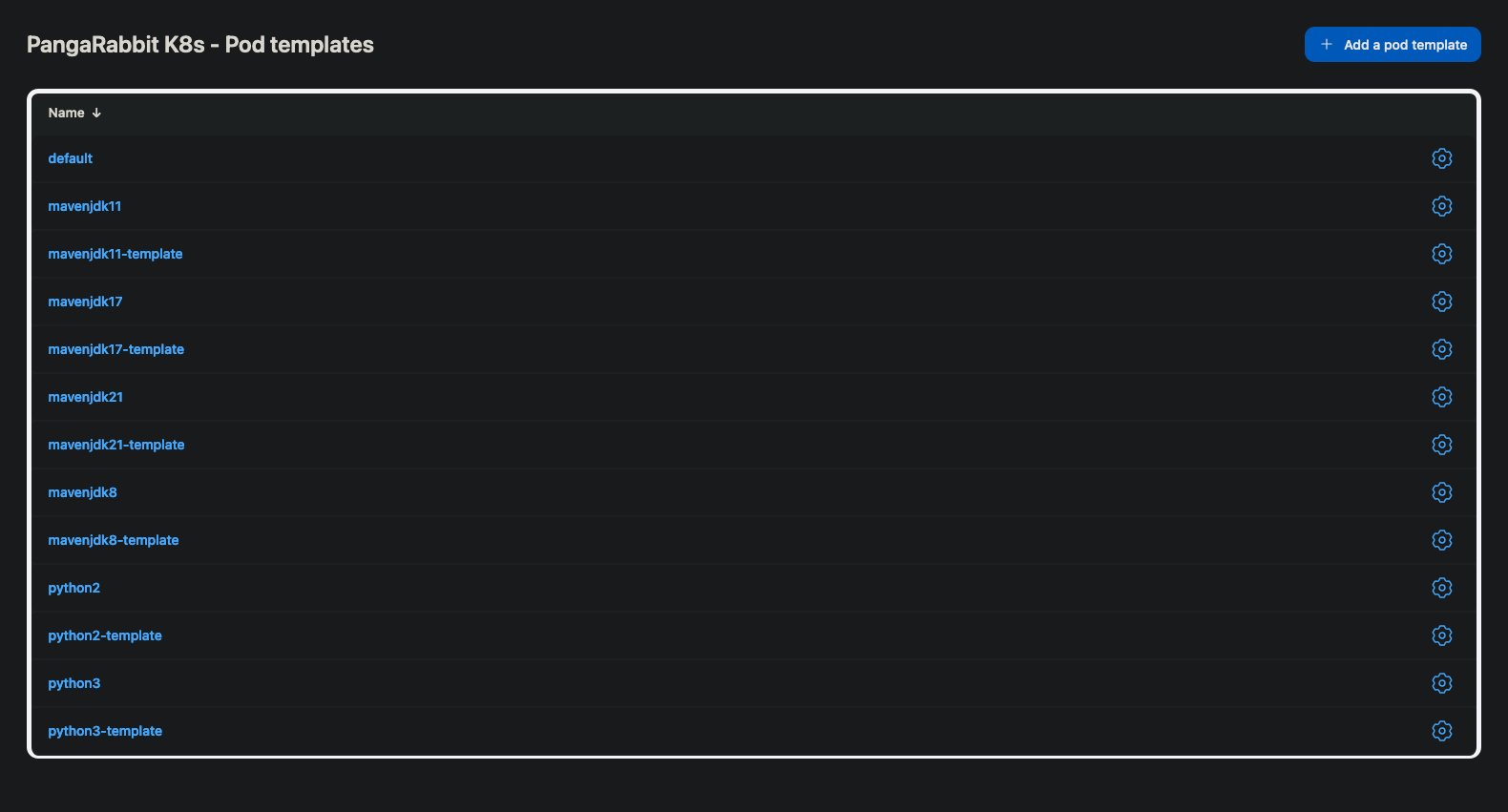
You can view your pod templates by following these steps.
- Click
Manage Jenkinsin the left hand menu

- Click
Clouds

- Click the name of your cloud, mine is
PangaRabbit K8s - Click
Pod Templates
Jenkins Backup Setup
- Click
Manage Jenkinsin the left hand menu

- Click
Plugins

- Check that you see the following Plugin installed if not install
ThinBackups

- You don’t need to do this as the backup tool will create the directory for you but it is a nice excercise to understand the volume mount process and to see how it works
- Open your terminal and lets exec onto the Jenkins pod
# Exec onto the pod
kubectl exec -it jenkins-0 -- /bin/bash
# Create a backup folder for ThinBackup
mkdir /var/jenkins_home/backup
- If your CSI NFS Kubernetes driver is setup correctly and you enabled persistence in the Helm Chart your Jenkins server configuration files will be stored here and you can make backups to the
backupdirectory - To see which PVC your Jenkins POD has mounted run this command
kubectl get pvc | grep jenkins
- When you navigate to your NFS server share you will see the
pvcname that was created for Jenkins - The name we want is under
VOLUME - For example mine was this

- You should see the
backupdirectory you created on your NFS storage server
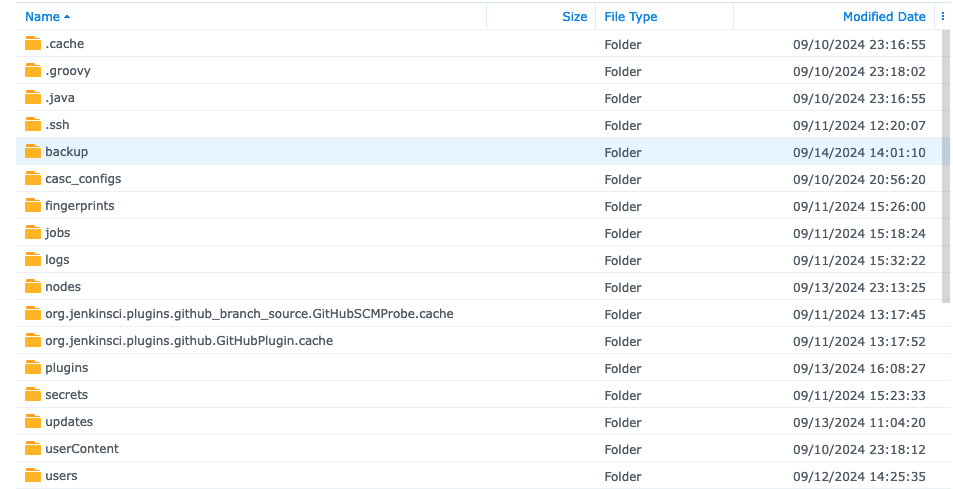
- Click
Manage Jenkins

- Click
System
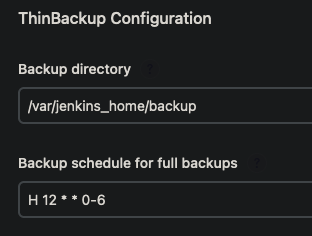
- Scroll down until you see
ThinBackup Configurationand fill in the following

- Add
/var/jenkins_home/backupas theBackup Directory - If you would like to backup your files once everyday at midnight use this cron
H 12 * * 0-6
- If you don’t like that idea you can make your own cron here
- Go through the rest of the settings and click on the
?for more information about the checkboxes - Click
Save - You should see backups appearing in your
backupdirectory on your NFS storage server at midnight if you used the cron above - Jenkins coveniently zips the backup set to save storage space
Jenkins Restore
I tested a restore by simply deleting all the Jenkins config off the NFS server, unzipped one of the backups and copied the Jenkins config files back then deleted the pod and waited for it to be recreated. It worked a charm, all my data, plugins, config, jobs and secrets were restored. I thought that was pretty neat. The Jenkins pod is simply a looking glass that presents all the Jenkins config in a human readable format. FYI make sure you backup your persistent volumes on the NFS server.

Creating a Multibranch Pipeline
- Open a terminal and create a new Kubernetes namespace called app
kubectl create ns app
- Back in Jenkins click on
New Item

- Give it a name
ortelius-jenkins-demo-app - Select
Multibranch Pipeline

- Configure the
Multibranch Pipelineas follows - Ignore the Jenkins
Shared Libraryconfiguration
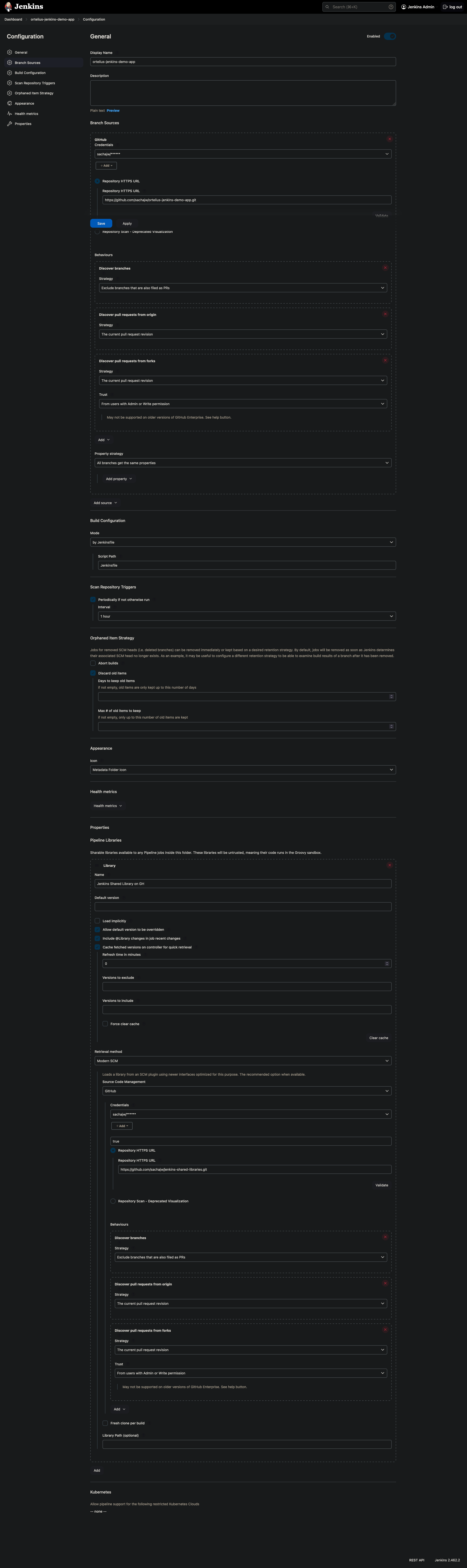
- Don’t forget to hit that
Savebutton

Jenkins meets Ortelius
- Create the following
Jenkinsfilein the GitHub repo your created and push it to your GitHub repo - A
Jenkinsfileis the logic to instruct Jenkins what to do - This
Jenkinsfilerecords the build data in Ortelius using theOrtelius CLIwhich can be found here
pipeline {
environment {
DHUSER = "admin" //Default Ortelius username
DHPASS = "admin" //Default Ortelius password
DHORG = "<organisation>" //Replace with your organisation
DHPROJECT = "ortelius-jenkins-demo-app" //Replace with your GitHub project name
DOCKERREPO = "<username>/hello-world" //Replace with your DockerHub repo username
DHURL = "https://ortelius.pangarabbit.com" //Replace with whatever you used to access the Ortelius frontend
}
agent {
kubernetes {
cloud 'PangaRabbit K8s' //Replace with your Cloud
defaultContainer 'python3' //Container default
inheritFrom 'python3' //Inherit from a template
namespace 'app' //The Kubernetes namespace you would like to deploy the app to
}
}
stages {
stage('Setup') {
steps {
sh '''
pip install ortelius-cli
git clone https://github.com/dstar55/docker-hello-world-spring-boot
cd docker-hello-world-spring-boot
dh envscript --envvars component.toml --envvars_sh ${WORKSPACE}/dhenv.sh
'''
}
}
stage('Build and push image') {
steps {
sh '''
source ${WORKSPACE}/dhenv.sh
docker build --tag ${DOCKERREPO}:${IMAGE_TAG} .
docker push ${DOCKERREPO}:${IMAGE_TAG}
# This line determines the docker digest for the image
echo export DIGEST=$(docker inspect --format='{{index .RepoDigests 0}}' ${DOCKERREPO}:${IMAGE_TAG} | cut -d: -f2 | cut -c-12) >> ${WORKSPACE}/dhenv.sh
'''
}
}
stage('Capture SBOM') {
steps {
sh '''
source ${WORKSPACE}/dhenv.sh
# install Syft
curl -sSfL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anchore/syft/main/install.sh | sh -s -- -b .
# create the SBOM
./syft packages ${DOCKERREPO}:${IMAGE_TAG} --scope all-layers -o cyclonedx-json > ${WORKSPACE}/cyclonedx.json
# display the SBOM
cat ${WORKSPACE}/cyclonedx.json
'''
}
}
stage('Create Component with Build Data and SBOM') {
steps {
sh '''
source ${WORKSPACE}/dhenv.sh
dh updatecomp --rsp component.toml --deppkg "cyclonedx@${WORKSPACE}/cyclonedx.json"
'''
}
}
}
}
- Lets git it
git add .
git commit -m "Add Jenkinsfile"
git push
- Go back to Jenkins and select the
Multibranch Pipelineyou just created - Select
Mainor whatever name appears there
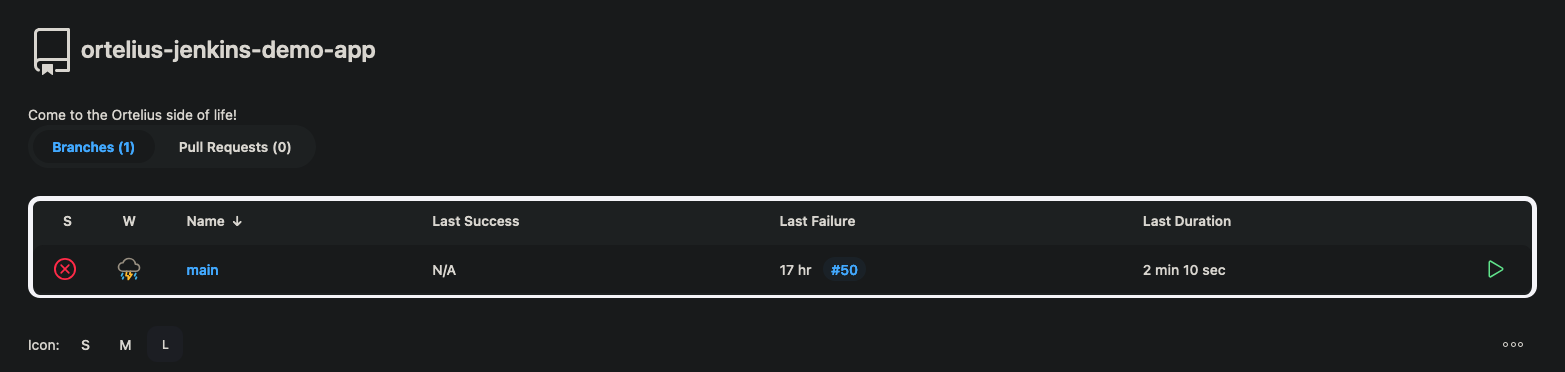
- Select
Build Now

- A build job will begin and you can see the build log by clicking on the
circlewith thecrossinside

- Open your terminal and run the following command
- This will show you the Python agent pod running which will build your Python app
- Don’t worry if there are some hiccups with the pod getting going we have limited resources
kubectl get pod -n app

- Here is a snippet of the build log from my Jenkins server
- You can see Jenkins stepping through the configuration in your
Jenkinsfile
Created Pod: PangaRabbit K8s app/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app-main-51-9gxfn-qzrgj-2hnmt
Agent ortelius-jenkins-demo-app-main-51-9gxfn-qzrgj-2hnmt is provisioned from template ortelius-jenkins-demo-app_main_51-9gxfn-qzrgj
---
apiVersion: "v1"
kind: "Pod"
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.jenkins.io/last-refresh: "1726324871013"
buildUrl: "http://jenkins.infrastructure.svc.cluster.local:8080/job/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app/job/main/51/"
runUrl: "job/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app/job/main/51/"
labels:
jenkins/jenkins-jenkins-agent: "true"
jenkins/label-digest: "fadc57588f0db543f93173def36c3565d0dfcc52"
jenkins/label: "ortelius-jenkins-demo-app_main_51-9gxfn"
kubernetes.jenkins.io/controller: "http___jenkins_infrastructure_svc_cluster_local_8080x"
name: "ortelius-jenkins-demo-app-main-51-9gxfn-qzrgj-2hnmt"
namespace: "app"
spec:
containers:
- args:
- "cat"
command:
- "/bin/sh"
- "-c"
env:
- name: "JENKINS_URL"
value: "http://jenkins.infrastructure.svc.cluster.local:8080/"
image: "python:3"
imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
name: "python3"
resources:
limits:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "512m"
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "512m"
tty: true
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent"
name: "workspace-volume"
readOnly: false
workingDir: "/home/jenkins/agent"
- env:
- name: "JENKINS_SECRET"
value: "********"
- name: "JENKINS_TUNNEL"
value: "jenkins-agent.infrastructure.svc.cluster.local:50000"
- name: "JENKINS_AGENT_NAME"
value: "ortelius-jenkins-demo-app-main-51-9gxfn-qzrgj-2hnmt"
- name: "REMOTING_OPTS"
value: "-noReconnectAfter 1d"
- name: "JENKINS_NAME"
value: "ortelius-jenkins-demo-app-main-51-9gxfn-qzrgj-2hnmt"
- name: "JENKINS_AGENT_WORKDIR"
value: "/home/jenkins/agent"
- name: "JENKINS_URL"
value: "http://jenkins.infrastructure.svc.cluster.local:8080/"
image: "jenkins/inbound-agent:3261.v9c670a_4748a_9-2"
name: "jnlp"
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "100m"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent"
name: "workspace-volume"
readOnly: false
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: "linux"
restartPolicy: "Never"
serviceAccountName: "default"
volumes:
- emptyDir:
medium: ""
name: "workspace-volume"
Running on ortelius-jenkins-demo-app-main-51-9gxfn-qzrgj-2hnmt in /home/jenkins/agent/workspace/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app_main
[Pipeline] {
[Pipeline] stage
[Pipeline] { (Declarative: Checkout SCM)
[Pipeline] checkout
The recommended git tool is: NONE
using credential gh-pangarabbit-jenkins
Cloning the remote Git repository
Cloning with configured refspecs honoured and without tags
Cloning repository https://github.com/sachajw/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app.git
> git init /home/jenkins/agent/workspace/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app_main # timeout=10
Fetching upstream changes from https://github.com/sachajw/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app.git
> git --version # timeout=10
> git --version # 'git version 2.39.2'
using GIT_ASKPASS to set credentials
> git fetch --no-tags --force --progress -- https://github.com/sachajw/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app.git +refs/heads/main:refs/remotes/origin/main # timeout=10
> git config remote.origin.url https://github.com/sachajw/ortelius-jenkins-demo-app.git # timeout=10
> git config --add remote.origin.fetch +refs/heads/main:refs/remotes/origin/main # timeout=10
Avoid second fetch
Checking out Revision 3d51ff295a43b243bd1ba65602a000b93522af9e (main)
> git config core.sparsecheckout # timeout=10
> git checkout -f 3d51ff295a43b243bd1ba65602a000b93522af9e # timeout=10
Commit message: "🛠 NEW: jenkins pod templates"
> git rev-list --no-walk 3d51ff295a43b243bd1ba65602a000b93522af9e # timeout=10
Conclusion
Hopefully you got this far and I did not forget some crucial configuration or step along the way. If I did please ping me so I can make any fixes. This illustrates how Ortelius can be used in an Enterprise environment to record SBOMS in a CI tool such as Jenkins. At this time of writing we are fixing the SBOM and Scorecard microservices to work with ARM architecture that is used on the Pi 4 to make them backward compatible. Hence if you are using that architecture you can’t record your SBOM and Scorecard info.
Happy alien hunting…..
Next Steps
How to Bake an Ortelius Pi | Part 6 | Cloud Dev At Home With Localstack
