Ortelius Blog
Topics include Supply Chain Security, Vulnerability Management, Neat Tricks, and Contributor insights.
How to Bake an Ortelius Pi Part 6 | Cloud Dev At Home With Localstack
- Introduction
- Gimlet GitOps Infrastructure
- AWS and Localstack CLI Configuration
- Localstack Tools
- Conclusion
- Next Steps
Introduction
In part 5 we deployed Jenkins on our Kubernetes cluster and configured integration with Ortelius and GitHub and built a demo application to demonstrate Ortelius’s ability to record it.
In part 6 we will deploy LocalStack and expose the endpoints through Traefik. We will use the AWS cli and the Localstack wrapper awslocal to create and list S3 buckets. To make using profiles with the cli easier we will use Granted created by Commonfate. This will give us our very own cloud dev environment at home without all the cash burning worries and security headaches.
Gimlet GitOps Infrastructure
Localstack
In today’s cloud-centric world, developing and testing applications that rely on cloud services often presents unique challenges. Developers typically need access to various cloud environments like AWS to test their code. However, setting up and managing these cloud environments can be cumbersome, costly, and time-consuming, especially for frequent testing or when multiple cloud services are involved.
Enter LocalStack, a powerful tool that provides a fully functional local cloud environment. LocalStack emulates the core AWS services, such as S3, Lambda, DynamoDB, and many others, enabling developers to run and test their cloud applications directly on their local machines without needing an active AWS account or network access.
Deploy Localstack
Right lets get stuck in and deploy Localtack using Gimlet, Fluxcd, Helm and a sprig of GitOps.
- Kubectl quick reference guide here
- Helm cheat sheet here
- Localstack on GitHub here
- Localstack docs here
- Localstack integrations here
- Localstack academy here
- Localstack tutorials here
- Localstack applications here
- Localstack extensions here
- Localstack Helm Chart on ArtifactHub here
Helm-Repository | Localstack
- Lets add the Localstack Helm repository
- A Helm repository is a collection of Helm charts that are made available for download and installation
- Helm repositories serve as centralised locations where Helm charts can be stored, shared, and managed
- Create a file called
localstack.yamlin the helm-repositories directory and paste the following YAML
---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta1
kind: HelmRepository
metadata:
name: localstack
namespace: infrastructure
spec:
interval: 60m
url: https://localstack.github.io/helm-charts
Helm-Release | Localstack
- Lets create a Helm release for LocalStack
- A Helm release is an instance of a Helm chart running in a Kubernetes cluster
- Each release is a deployment of a particular version of a chart with a specific configuration
- Create a file called
localstack.yamlin the helm-releases directory and paste the following YAML
Helm Chart Configuration Highlights
image:
repository: localstack/localstack # Replace this with localstack/localstack-pro if you have a subscription
tag: "latest"
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
replicaCount: 3
mountDind:
enabled: true
forceTLS: true
image: "docker:20.10-dind"
extraEnvVars:
- name: GATEWAY_LISTEN
value: "0.0.0.0:4566"
- name: LOCALSTACK_API_KEY
value: "<your api key"
- name: LOCALSTACK_AUTH_TOKEN
value: "<your auth token>"
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations: {}
## @param ingress.ingressClassName Set the name of the class to use
##
ingressClassName: "traefik" # Only replace this if you are not using Traefik
hosts:
- host: localstack.pangarabbit.com # Replace with your domain
persistence:
## @param persistence.enabled Enable persistence using Persistent Volume Claims
##
enabled: true # Set to false to disable persistent volumes
## @param persistence.storageClass Persistent Volume storage class
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is set, choosing the default provisioner
##
storageClass: "nfs-csi-localstack" # Replace with your storage class
## @param persistence.accessModes [array] Persistent Volume access modes
##
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
## @param persistence.size Persistent Volume size
##
size: 8Gi
---
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta2
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: localstack
namespace: infrastructure
spec:
interval: 60m
releaseName: localstack
chart:
spec:
chart: localstack
version: 0.6.16 # Simply change the version to upgrade
sourceRef:
kind: HelmRepository
name: localstack
interval: 10m
values:
# Default values for LocalStack
# Declare variables to be passed into your templates
replicaCount: 3
## @param updateStrategy.type deployment strategy type
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/deployment/#strategy
## NOTE: Set it to `Recreate` if you use a PV that cannot be mounted on multiple pods
##
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
image:
repository: localstack/localstack-pro
tag: "latest"
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
imagePullSecrets: []
nameOverride: ""
fullnameOverride: ""
## @param extraDeploy Extra objects to deploy (value evaluated as a template)
##
extraDeploy: []
## Add additional annotations to every resource
extraAnnotations: {}
serviceAccount:
# Specifies whether a service account should be created
create: true
# Annotations to add to the service account
annotations: {}
# The name of the service account to use.
# If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
name: ""
role:
# Specifies whether a role & rolebinding with pods / * permissions should be created for the service account
# Necessary for kubernetes lambda executor
create: true
# Annotations to add to the role and rolebinding
annotations: {}
# The name of the role and rolebinding to use.
# If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
name: ""
podLabels: {}
podAnnotations: {}
podSecurityContext:
{}
# fsGroup: 2000
securityContext:
{}
# capabilities:
# drop:
# - ALL
# readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
# runAsNonRoot: true
# runAsUser: 1000
debug: false
## @param command Allows you to set an arbitrary command on startup (instead of the default entrypoint script)
##
command: []
## @param dnsPolicy Allows you to set the Pod dnsPolicy.
## The default is actually ClusterFirst. Uncomment this to avoid a circular DNS path that will
## cause the LocalStack instance to crash.
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/dns-pod-service/#pod-s-dns-policy
# dnsPolicy: "Default"
startServices: ""
# Comma-separated list of AWS CLI service names which are the only ones allowed to be used (other services will then by default be prevented from being loaded).
# kinesisErrorProbability: 0.0
# lambdaExecutor: ""
# This will enable the Docker daemon binding and allow
# Localstack to provide Lambdas and other AWS services
# who got container runtime dependencies
mountDind:
enabled: true
forceTLS: true
image: "docker:20.10-dind"
## All the parameters from the configuation can be added using extraEnvVars.
## Ref. https://docs.localstack.cloud/references/configuration/
extraEnvVars:
- name: GATEWAY_LISTEN
value: "0.0.0.0:4566"
# Use this if you have an API key and comment out the auth token
- name: LOCALSTACK_API_KEY
value: "<your api key"
# Use this if you have an auth token and comment out the API key
- name: LOCALSTACK_AUTH_TOKEN
value: "your auth token"
## - name: SERVICES
## value: "serverless,sqs,es"
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 0
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 1
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 0
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 1
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
service:
type: ClusterIP
annotations:
ipFamilies: []
ipFamilyPolicy: ""
externalTrafficPolicy: ""
edgeService:
name: edge
targetPort: 4566
nodePort: 31566
externalServicePorts:
start: 4510
end: 4560
## @param service.externalServicePorts.nodePortStart specifies the starting node ports the serviceports are mapped to
## has to be in the node port range configured. See https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#type-nodeport
# nodePortStart: 31510
## @param service.dnsService Enables or disables the exposure of the LocalStack DNS
##
dnsService: false
## @param service.clusterIP sets a static clusterIP. This is useful alongside the LocalStack DNS setup
## see https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/dns-custom-nameservers/#configuration-of-stub-domain-and-upstream-nameserver-using-coredns for an example of DNS delegation in Coredns
##
clusterIP: ""
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations: {}
## @param ingress.ingressClassName Set the name of the class to use
##
ingressClassName: "traefik"
hosts:
- host: localstack.pangarabbit.com
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
# tls:
# - secretName: wildcard-pangarabbit-com-tls
# hosts:
# - localstack.pangarabbit.com
persistence:
## @param persistence.enabled Enable persistence using Persistent Volume Claims
##
enabled: true
## @param persistence.storageClass Persistent Volume storage class
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is set, choosing the default provisioner
##
storageClass: "nfs-csi-localstack" # Add your storage class here
## @param persistence.accessModes [array] Persistent Volume access modes
##
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
## @param persistence.size Persistent Volume size
##
size: 8Gi
## @param persistence.dataSource Custom PVC data source
##
dataSource: {}
## @param persistence.existingClaim The name of an existing PVC to use for persistence
##
existingClaim: ""
## @param persistence.subPath The name of a volume's sub path to mount for persistence
##
subPath: ""
## @param persistence.annotations Annotations to be added to PVC
##
annotations: {}
resources:
{}
# We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious
# choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little
# resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following
# lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'.
# limits:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi
# All settings inside the lambda values section are only applicable to the new v2 lambda provider
lambda:
# The lambda runtime executor.
# Depending on the value, LocalStack will execute lambdas either in docker containers or in kubernetes pods
# The value "kubernetes" depends on the service account and pod role being activated
executor: "docker"
# Image prefix for the kubernetes lambda images. The images will have to be pushed to that repository.
# Only applicable when executor is set to "kubernetes"
# Example: python3.9 runtime -> localstack/lambda-python:3.9
image_prefix: "localstack/lambda-"
# Timeout for spawning new lambda execution environments.
# After that timeout, the environment (in essence pod/docker container) will be killed and restarted
# Increase if spawning pods / docker containers takes longer in your environment
environment_timeout: 60
# Labels which will be assigned to the kubernetes pods spawned by the kubernetes executor.
# They will be set on all spawned pods.
# Only applicable when executor is set to "kubernetes"
labels: {}
# labels:
# label1: value1
# label2: value2
# label3: value3
#
# Security context to be set on the kubernetes pods spawned by the kubernetes executor.
# It will be set on all spawned pods.
# Only applicable when executor is set to "kubernetes"
security_context: {}
# security_context:
# runAsUser: 1000
# fsGroup: 1000
# label3: value3
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
# Mount /etc/localstack/init/ready.d to run startup scripts with
# {{ template "localstack.fullname" . }}-init-scripts-config configMap
enableStartupScripts: false
# Add startup scripts content used by {{ template "localstack.fullname" . }}-init-scripts-config configMap
# to run at localstack startup
# startupScriptContent: |
# awslocal s3 mb s3://testbucket
# awslocal sqs create-queue --queue-name test-queue
startupScriptContent: ""
# @param volumes Extra volumes to mount
volumes: []
# - hostPath:
# path: <HOST_PATH>
# name: <VOLUME_NAME>
# @param volumeMounts Extra volumes to mount
volumeMounts: []
# - name: <VOLUME_NAME>
# mountPath: <CONTAINER_PATH>
# readOnly: true
## @param priorityClassName Allows you to set the priorityClassName for the pod
## The default is not to set any priorityClassName
# priorityClassName: ""
- Lets git it
git add .
git commit -m "localstack deploy"
git push
Fluxcd is doing the following under the hood | Localstack
- Helm repo add
helm repo add localstack-charts https://localstack.github.io/helm-charts --force-update
- Helm install localstack
helm install localstack localstack-charts/localstack
Kubernetes check | Localstack
- Kubectl switch to the infrastructure namespace
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=infrastructure
- Kubectl show me the pods for Localstack
kubectl get pods -n infrastructure | grep localstack

- Kubectl show me the persistent claims
kubectl get pvc | grep localstack

- Now that we have deployed Localstack we will expose the Localstack endpoints with Traefik
Traefik
- Open your Traefik Helm Chart from the
helm-releasesdirectory for your infrastructure repo that Gimlet created - For example mine is
gitops-pangarabbit-dev-infra/helm-releases - Add the following entrypoint after the
websecureentrypoint in yourtraefik.yamlhelm-releasesfile
localstack:
## -- Enable this entrypoint as a default entrypoint. When a service doesn't explicitly set an entrypoint it will only use this entrypoint.
# asDefault: true
port: 4566
# hostPort: 4566
containerPort: 4566
expose:
default: true
exposedPort: 4566
## -- Different target traefik port on the cluster, useful for IP type LB
# targetPort: 80
## -- The port protocol (TCP/UDP)
protocol: TCP
- Lets git it
git add .
git commit -m "traefik localstack entrypoint"
git push
- Navigate to the
traefik-dynamic-config.yamlfile in themanifests/directory and add theIngressRoutefor Localstack and push your changes
---
apiVersion: traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: localstack
namespace: infrastructure
spec:
entryPoints:
- localstack
routes:
- match: Host("localstack.pangarabbit.com") # Replace this with your domain
kind: Rule
services:
- name: localstack
namespace: infrastructure
kind: Service
port: 4566
- Lets git it
git add .
git commit -m "traefik localstack ingressroute"
git push
- You should see the Localstack endpoint represented on your Traefik dashboard
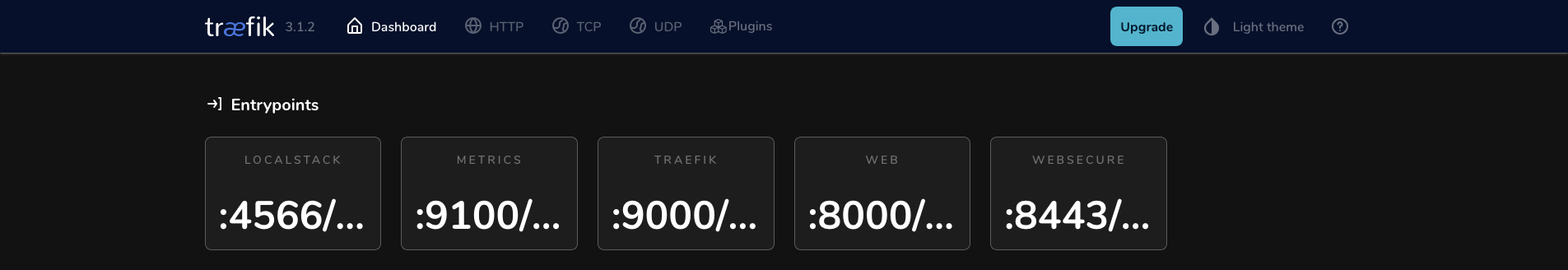
- Don’t forget to add a DNS record for the Localstack domain name you used
- If everything went well you should be able to curl the Localstack endpoint with the domain name that you chose for example mine is
https://localstack.pangarabbit.com - Open our terminal and use curl to test the Localstack endpoint
- You don’t need the
:4566port at the end of the url as Traefik takes care of that when we created theIngressRoute
curl -vvv https://localstack.pangarabbit.com
- The output below shows you the endpoint is alive and well and secure
* Host localstack.pangarabbit.com:443 was resolved.
* IPv6: (none)
* IPv4: 192.168.0.151
* Trying 192.168.0.151:443...
* Connected to localstack.pangarabbit.com (192.168.0.151) port 443
* ALPN: curl offers h2,http/1.1
* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
* CAfile: /etc/ssl/cert.pem
* CApath: none
* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Unknown (8):
* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):
* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / AEAD-CHACHA20-POLY1305-SHA256 / [blank] / UNDEF
* ALPN: server accepted h2
* Server certificate:
* subject: CN=pangarabbit.com
* start date: Aug 1 16:47:29 2024 GMT
* expire date: Oct 30 16:47:28 2024 GMT
* subjectAltName: host "localstack.pangarabbit.com" matched cert's "*.pangarabbit.com"
* issuer: C=US; O=Let's Encrypt; CN=R10
* SSL certificate verify ok.
* using HTTP/2
* [HTTP/2] [1] OPENED stream for https://localstack.pangarabbit.com/
* [HTTP/2] [1] [:method: GET]
* [HTTP/2] [1] [:scheme: https]
* [HTTP/2] [1] [:authority: localstack.pangarabbit.com]
* [HTTP/2] [1] [:path: /]
* [HTTP/2] [1] [user-agent: curl/8.7.1]
* [HTTP/2] [1] [accept: */*]
> GET / HTTP/2
> Host: localstack.pangarabbit.com
> User-Agent: curl/8.7.1
> Accept: */*
>
* Request completely sent off
< HTTP/2 200
< alt-svc: h3=":8443"; ma=2592000
< content-type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
< date: Sat, 14 Sep 2024 20:00:22 GMT
< server: TwistedWeb/24.3.0
< content-length: 0
<
* Connection #0 to host localstack.pangarabbit.com left intact
AWS and Localstack CLI Configuration
- Lets test to see if we can create a S3 bucket using the Localstack AWS wrapper command line tool called
awslocaland the AWS cli - To make our lives less painful switching profiles install Granted created by Commonfate
- Use the Granted
getting starteddoc here - Please install the Localstack AWS cli wrapper tool here
- For more information on installation and configuring the AWS cli go here
- Create fictitious credentials in
.aws/credentialsfor Localstack
[base]
aws_access_key_id=fake
aws_secret_access_key=fake
- Create a profile in
.aws/config
[profile localstack]
endpoint_url = https://localstack.pangarabbit.com:4566 # Replace with your endpoint domain name
services = localstack
region = us-east-1
output = yaml
cli_history = enabled
cli_pager = bat
credential_process = granted credential-process --profile=localstack
[services localstack]
s3 =
endpoint_url = https://localstack.pangarabbit.com:4566 # Replace with your endpoint domain name
addressing_style = path
- Install Granted for your OS flavour
- Test that Granted was installed correctly
granted -v
- Assume your first role here
- You role name will be
localstack - After completing the first time setup you should be able to just type
assumeon the command line and a selection will pop up
assume
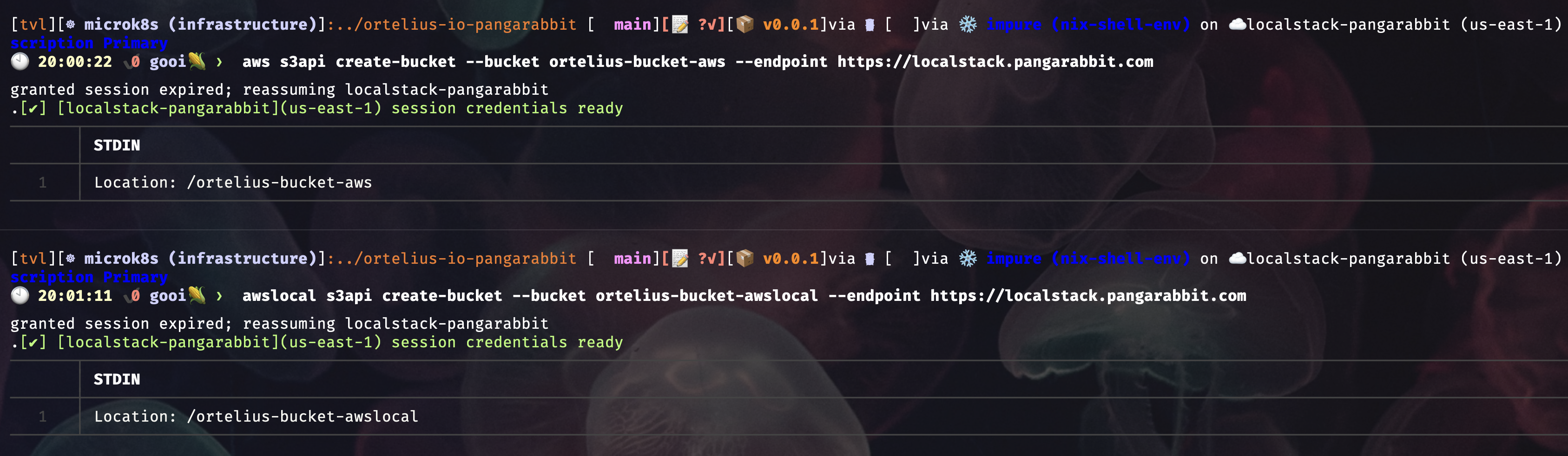
- S3 bucket creation
aws s3api create-bucket --bucket ortelius-bucket-aws --endpoint https://localstack.pangarabbit.com
awslocal s3api create-bucket --bucket ortelius-bucket-awslocal --endpoint https://localstack.pangarabbit.com
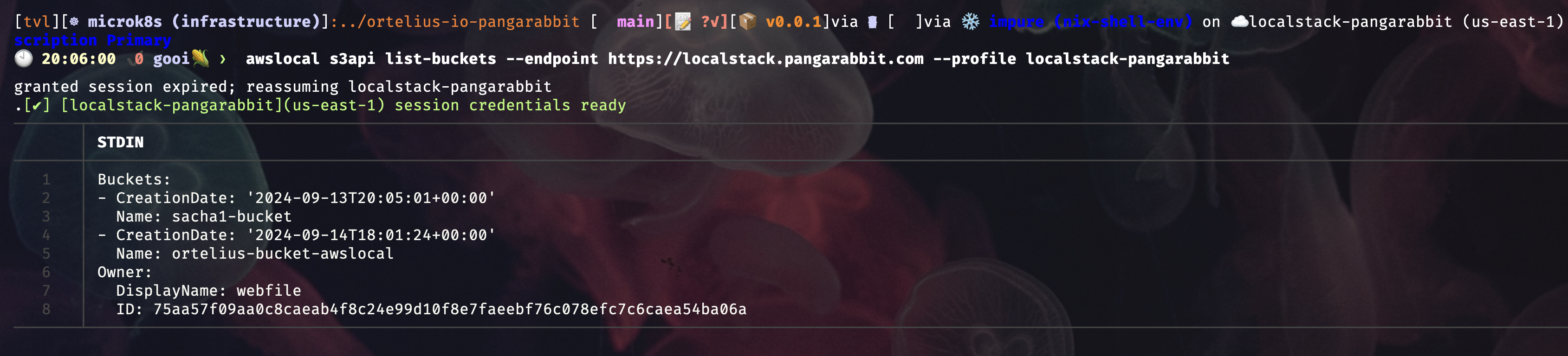
- Lets list s3 buckets with
awslocal
awslocal s3api list-buckets --endpoint https://localstack.pangarabbit.com --profile localstack-pangarabbit
- Lets list s3 buckets with
aws
aws s3api list-buckets --endpoint https://localstack.pangarabbit.com --profile localstack-pangarabbit
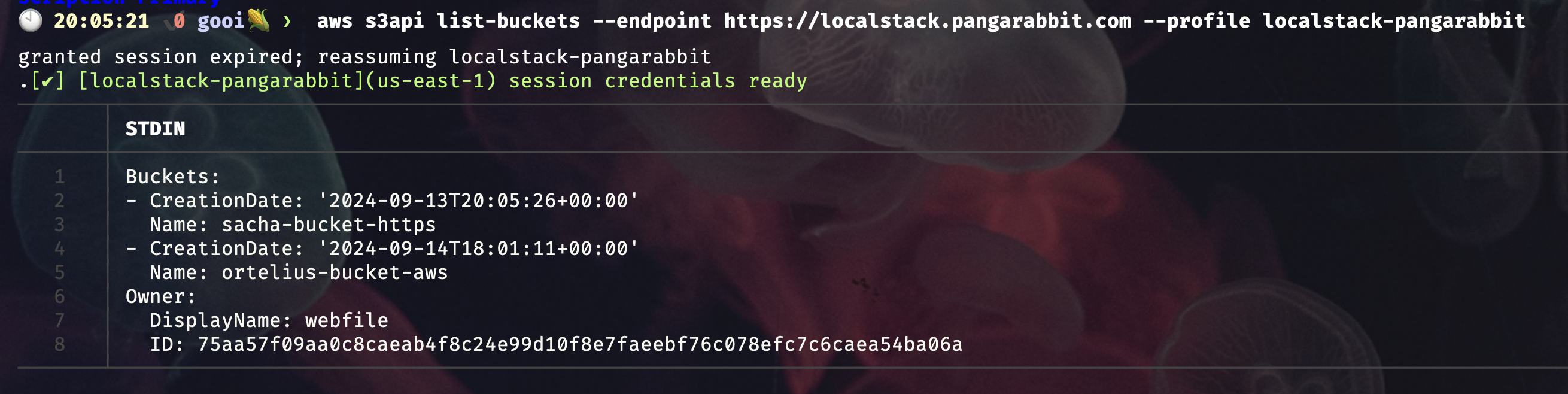
Localstack Tools
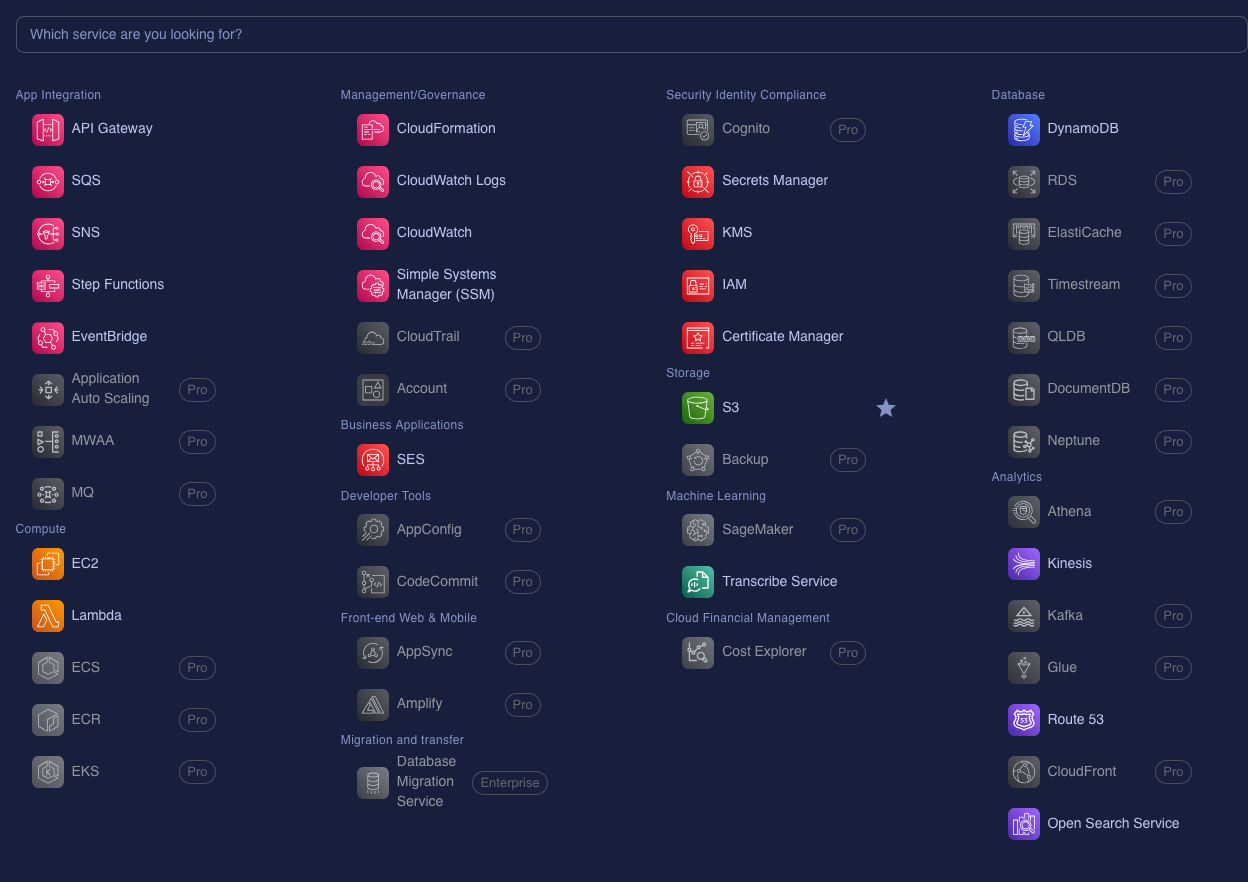
You can find LocalStack tools here. One of these tools, Localstack Desktop, provides a GUI that allows you to view and manage your Localstack resources and services on your local machine. It also lets you add custom endpoints that you’ve created.
To get Localstack Desktop, sign up for Localstack with your browser, where you’ll have access to the Localstack portal. From there, you can manage everything related to your Localstack setup, including viewing instances and adding custom endpoints.
You can access the LocalStack portal at this URL: https://app.localstack.cloud/dashboard. Once inside, look for the LocalStack Desktop menu item.
- Localstack custom endpoint in the browser

- Localstack custom endpoint in Localstack Desktop

- Localstack services in the browser
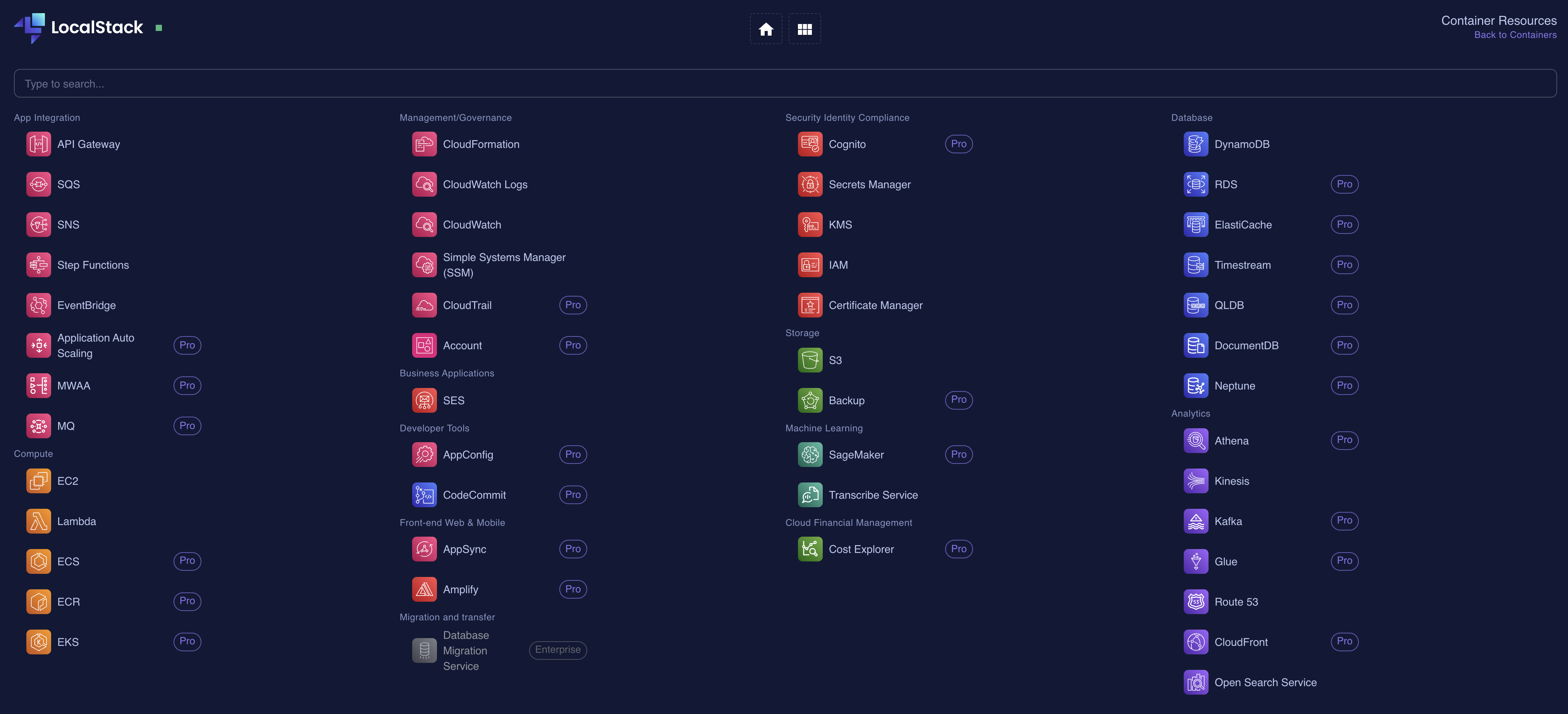
- Localstack services in Localstack Desktop
FYI make sure you backup your persistent volumes on the NFS server
Conclusion
You now have a local working cloud to develop against, test applications and learn safely. If I missed any steps or something needs correction please ping me so I can make any fixes. This illustrates how you can deploy LocalStack and publish the endpoint through Traefik.
Happy alien hunting…..
Next Steps
How to Bake an Ortelius Pi | Part 7 | Observability with Netdata
